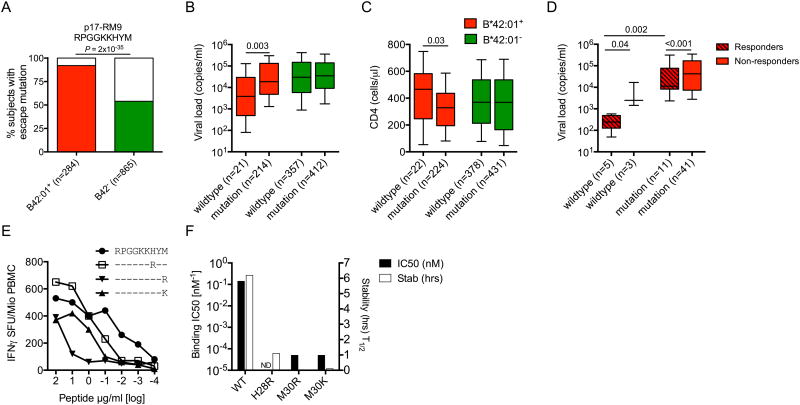
Figure 4. HIV-1 sequence polymorphisms in Gag-RM9 are CD8+ T-cell escape mutations associated with loss of immune control.
(A) HLA-B*42:01+ (red) and HLA-B*42:01- (green) associations with mutations in Gag-RM9 (departure from wildtype). Significance was determined using Fisher's exact test. (B) Viral load set-points and (C) CD4+ T-cell counts in HLA-B*42:01+ (red) and HLA-B*42:01- (green) individuals carrying either wildtype Gag-RM9 (RPGGKKHYM) or any mutation in this epitope. The x-axis indicates the number of sequences analyzed in each case. (D) Viral load set-points in 60 HLA-B*42:01+ individuals carrying either wildype Gag-RM9 or any mutation in this epitope stratified for responder (crossed boxes) or non-responder (open boxes) status. (E) Impact of the commonly selected H28R, M30R and M30K variants on CD8+ T-cell recognition in IFNγ ELISpot assays. Data from subject R019 (A*02:01/30:01, B*35:01/42:01, Cw*16:01/17:01) are shown. (F) HLA-B*42:01 binding affinities and half-lives (stability) for the peptides shown in (E). In (B-D), horizontal bars indicate median values presented by 25th percentile boxes and ranges (standard deviation); significance was determined using the Mann-Whitney U-test.