Abstract
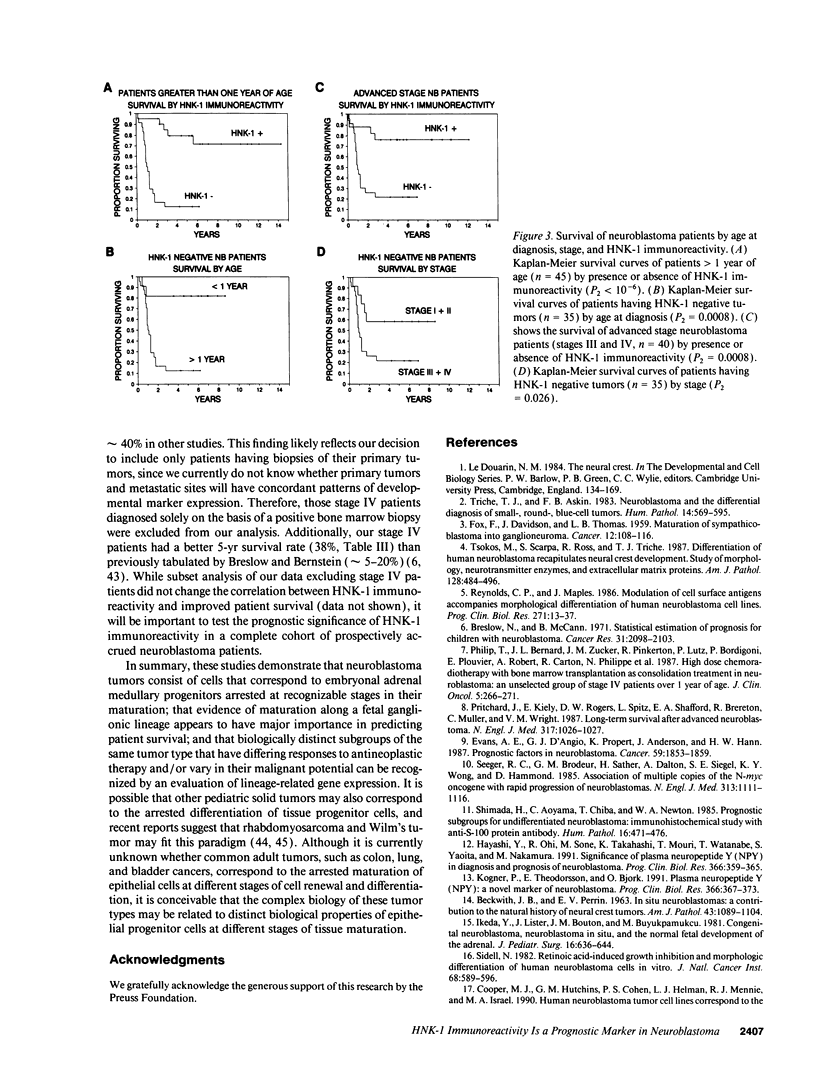
We have recently presented a model of human adrenal medullary histogenesis that incorporates all neural crest-derived lineages (chromaffin, sustentacular, and ganglionic) known to compose this tissue. To determine if neuroblastomas correspond to the arrested maturation of embryonal adrenal medullary cells, we evaluated the expression of adrenal medullary developmental markers in 81 neuroblastoma tumors. We found that patterns of chromaffin-related gene expression in these tumors correlated exactly with the patterns observed during maturation of adrenal medullary cells (P2 < 10(-5). In a multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis of developmental marker expression and other well-recognized prognostic variables, evidence of maturation along a fetal ganglionic lineage, as monitored by HNK-1 immunoreactivity (relative risk of 6.42, P2 = 0.0001), and age at diagnosis (relative risk of 5.05, P2 = 0.0042) were independent and significant prognostic indicators of patient survival. These studies demonstrate that neuroblastomas correspond to embryonal adrenal medullary cells arrested at recognizable stages during development, and that evidence of maturation along a fetal ganglionic lineage appears to have major importance in predicting patient survival.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Axel R. A bipotential neuroendocrine precursor whose choice of cell fate is determined by NGF and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90823-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J. The neural crest cell lineage problem: neuropoiesis? Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKWITH J. B., PERRIN E. V. IN SITU NEUROBLASTOMAS: A CONTRIBUTION TO THE NATURAL HISTORY OF NEURAL CREST TUMORS. Am J Pathol. 1963 Dec;43:1089–1104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroffio A., Dupin E., Le Douarin N. M. Clone-forming ability and differentiation potential of migratory neural crest cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5325–5329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith J. B., Kiviat N. B., Bonadio J. F. Nephrogenic rests, nephroblastomatosis, and the pathogenesis of Wilms' tumor. Pediatr Pathol. 1990;10(1-2):1–36. doi: 10.3109/15513819009067094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein M. L., Leclerc J. M., Bunin G., Brisson L., Robison L., Shuster J., Byrne T., Gregory D., Hill G., Dougherty G. A population-based study of neuroblastoma incidence, survival, and mortality in North America. J Clin Oncol. 1992 Feb;10(2):323–329. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow N., McCann B. Statistical estimation of prognosis for children with neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 1971 Dec;31(12):2098–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner-Fraser M., Fraser S. E. Cell lineage analysis reveals multipotency of some avian neural crest cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):161–164. doi: 10.1038/335161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccarone V., Spengler B. A., Meyers M. B., Biedler J. L., Ross R. A. Phenotypic diversification in human neuroblastoma cells: expression of distinct neural crest lineages. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):219–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude P., Parada I. M., Gordon K. A., D'Amore P. A., Wagner J. A. Acidic fibroblast growth factor stimulates adrenal chromaffin cells to proliferate and to extend neurites, but is not a long-term survival factor. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):783–790. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Cooper M. J., Helman L. J., Thiele C. J., Seeger R. C., Israel M. A. Neuropeptide Y expression in the developing adrenal gland and in childhood neuroblastoma tumors. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 15;50(18):6055–6061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. J., Hutchins G. M., Israel M. A. Histogenesis of the human adrenal medulla. An evaluation of the ontogeny of chromaffin and nonchromaffin lineages. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):605–615. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. J., Hutchins G. M., Mennie R. J., Israel M. A. Beta 2-microglobulin expression in human embryonal neuroblastoma reflects its developmental regulation. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 15;50(12):3694–3700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Angio G. J., Evans A. E., Koop C. E. Special pattern of widespread neuroblastoma with a favourable prognosis. Lancet. 1971 May 22;1(7708):1046–1049. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91606-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias P., Parham D. M., Shapiro D. N., Webber B. L., Houghton P. J. Myogenic regulatory protein (MyoD1) expression in childhood solid tumors: diagnostic utility in rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Pathol. 1990 Dec;137(6):1283–1291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Landis S. C., Patterson P. H. Environmental influences in the development of neural crest derivatives: glucocorticoids, growth factors, and chromaffin cell plasticity. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2119–2142. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Patterson P. H., Landis S. C. Small intensely fluorescent cells in culture: role of glucocorticoids and growth factors in their development and interconversions with other neural crest derivatives. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2143–2160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Badry O. M., Romanus J. A., Helman L. J., Cooper M. J., Rechler M. M., Israel M. A. Autonomous growth of a human neuroblastoma cell line is mediated by insulin-like growth factor II. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):829–839. doi: 10.1172/JCI114243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. E., Chatten J., D'Angio G. J., Gerson J. M., Robinson J., Schnaufer L. A review of 17 IV-S neuroblastoma patients at the children's hospital of philadelphia. Cancer. 1980 Mar 1;45(5):833–839. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800301)45:5<833::aid-cncr2820450502>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. E., D'Angio G. J., Propert K., Anderson J., Hann H. W. Prognostic factor in neuroblastoma. Cancer. 1987 Jun 1;59(11):1853–1859. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870601)59:11<1853::aid-cncr2820591102>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. E., D'Angio G. J., Randolph J. A proposed staging for children with neuroblastoma. Children's cancer study group A. Cancer. 1971 Feb;27(2):374–378. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197102)27:2<374::aid-cncr2820270221>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. E., Gerson J., Schnaufer L. Spontaneous regression of neuroblastoma. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Nov;44:49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX F., DAVIDSON J., THOMAS L. B. Maturation of sympathicoblastoma into ganglioneuroma; report of 2 patients with 20-and 46-year survivals respectively. Cancer. 1959 Jan-Feb;12(1):108–116. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195901/02)12:1<108::aid-cncr2820120116>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert F., Balaban G., Moorhead P., Bianchi D., Schlesinger H. Abnormalities of chromosome 1p in human neuroblastoma tumors and cell lines. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1982 Sep;7(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(82)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Ohi R., Sone M., Takahashi K., Mouri T., Watanabe T., Yaoita S., Nakamura M. Significance of plasma neuropeptide Y (NPY) in diagnosis and prognosis of neuroblastoma. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;366:359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helman L. J., Thiele C. J., Linehan W. M., Nelkin B. D., Baylin S. B., Israel M. A. Molecular markers of neuroendocrine development and evidence of environmental regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2336–2339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Lister J., Bouton J. M., Buyukpamukcu M. Congenital neuroblastoma, neuroblastoma in situ, and the normal fetal development of the adrenal. J Pediatr Surg. 1981 Aug;16(4 Suppl 1):636–644. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(81)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogner P., Theodorsson E., Björk O. Plasma neuropeptide Y (NPY): a novel marker of neuroblastoma. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;366:367–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantel N. Evaluation of survival data and two new rank order statistics arising in its consideration. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1966 Mar;50(3):163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson P. H. Control of cell fate in a vertebrate neurogenic lineage. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1035–1038. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90379-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip T., Bernard J. L., Zucker J. M., Pinkerton R., Lutz P., Bordigoni P., Plouvier E., Robert A., Carton R., Philippe N. High-dose chemoradiotherapy with bone marrow transplantation as consolidation treatment in neuroblastoma: an unselected group of stage IV patients over 1 year of age. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Feb;5(2):266–271. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard J., Kiely E., Rogers D. W., Spitz L., Shafford E. A., Brereton R., Muller C., Wright V. M. Long-term survival after advanced neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):1026–1027. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger R. C., Brodeur G. M., Sather H., Dalton A., Siegel S. E., Wong K. Y., Hammond D. Association of multiple copies of the N-myc oncogene with rapid progression of neuroblastomas. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 31;313(18):1111–1116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510313131802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada H., Aoyama C., Chiba T., Newton W. A., Jr Prognostic subgroups for undifferentiated neuroblastoma: immunohistochemical study with anti-S-100 protein antibody. Hum Pathol. 1985 May;16(5):471–476. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidell N. Retinoic acid-induced growth inhibition and morphologic differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Apr;68(4):589–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemple D. L., Mahanthappa N. K., Anderson D. J. Basic FGF induces neuronal differentiation, cell division, and NGF dependence in chromaffin cells: a sequence of events in sympathetic development. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triche T. J., Askin F. B. Neuroblastoma and the differential diagnosis of small-, round-, blue-cell tumors. Hum Pathol. 1983 Jul;14(7):569–595. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80202-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos M., Scarpa S., Ross R. A., Triche T. J. Differentiation of human neuroblastoma recapitulates neural crest development. Study of morphology, neurotransmitter enzymes, and extracellular matrix proteins. Am J Pathol. 1987 Sep;128(3):484–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]