Figure 3.
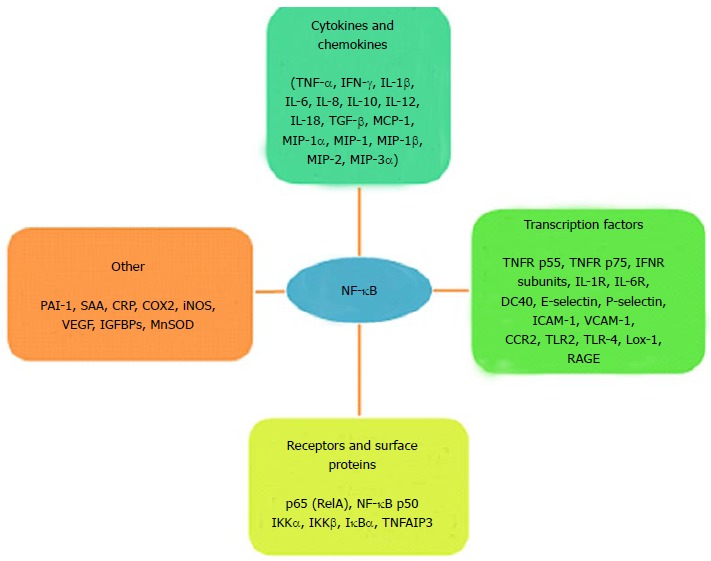
Target genes activated by NF-κB. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; IL: Interleukin; TGF-β: Tumor growth factor-beta; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MIP: Major intrinsic protein; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor; INFR: Interferon receptor; IL-R: Interleukin receptor; CD: Cluster of differentiation; ICAM: Intracellular cell adhesion molecule; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule; CCR: Chemokine CC receptor; TLR: Toll-like receptor; Lox: Lysyl oxidase; RAGE: Receptor advanced glycation end product; PAI: Plasminogen inhibitor activator; SAA: Serum amyloid; CRP: C-reactive protein; COX: Cyclo-oxygenase; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; IGFBPs: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein; MnSOD: Manganese superoxide dismutase; RelA: Reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; IKK: Inhibitor Kappa B kinase; IκBα: Inhibitor of NF-κB; TNFAIP3: TNF-α induced protein 3.
