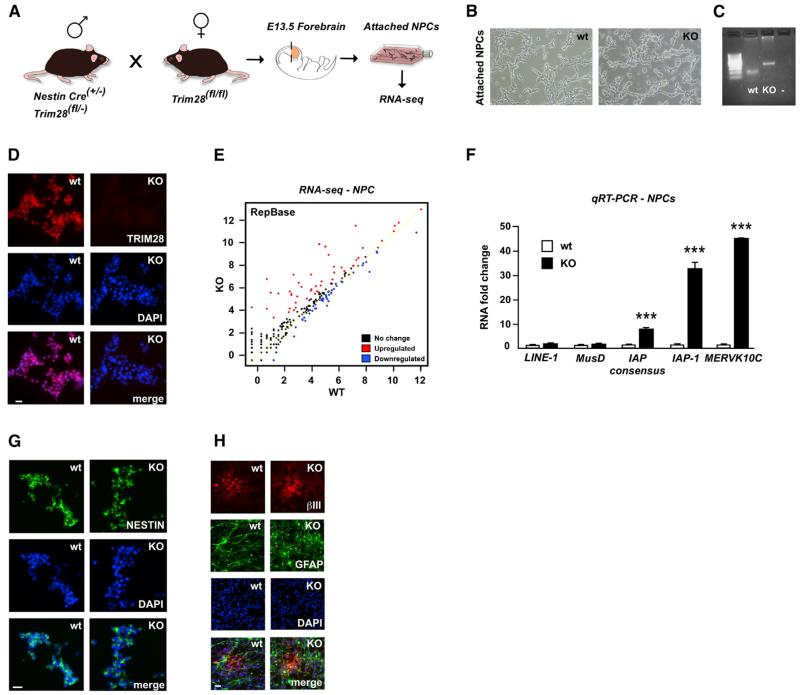
Figure 1. Establishment of Trim28-Deficient Neural Progenitor Cultures.
(A) Illustration of the experimental approach.
(B) Representative images of early passage Trim28−/− NPCs.
(C) PCR analysis of genomic DNA from wild-type and Trim28−/− NPCs demonstrates the presence of the 152 and 290 bp products corresponding to loxP-flanked or excised Trim28, respectively.
(D) Verification of a complete lack of TRIM28 protein via immunocytochemistry.
(E) RNA-seq analysis. The graph shows KO samples plotted versus wild-type samples, where each dot represents a Repbase sequence.
(F) qRT-PCR of RNA isolated from wild-type and Trim28−/− NPCs.
(G) Trim28-deficient NPCs display a homogenous expression of NESTIN.
(H) Immunofluorescent analysis of differentiated NPCs.
Data are presented as mean of relative values ± SEM. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Student’s t test. Scale bars, 200 (A) and 50 (B) μm. See also Tables S1 and S2.