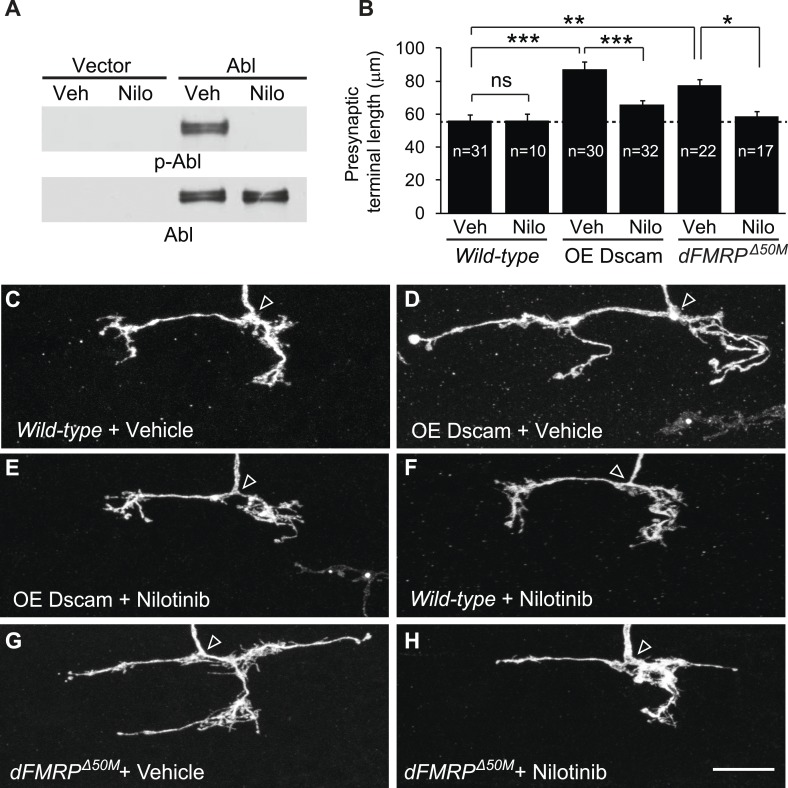
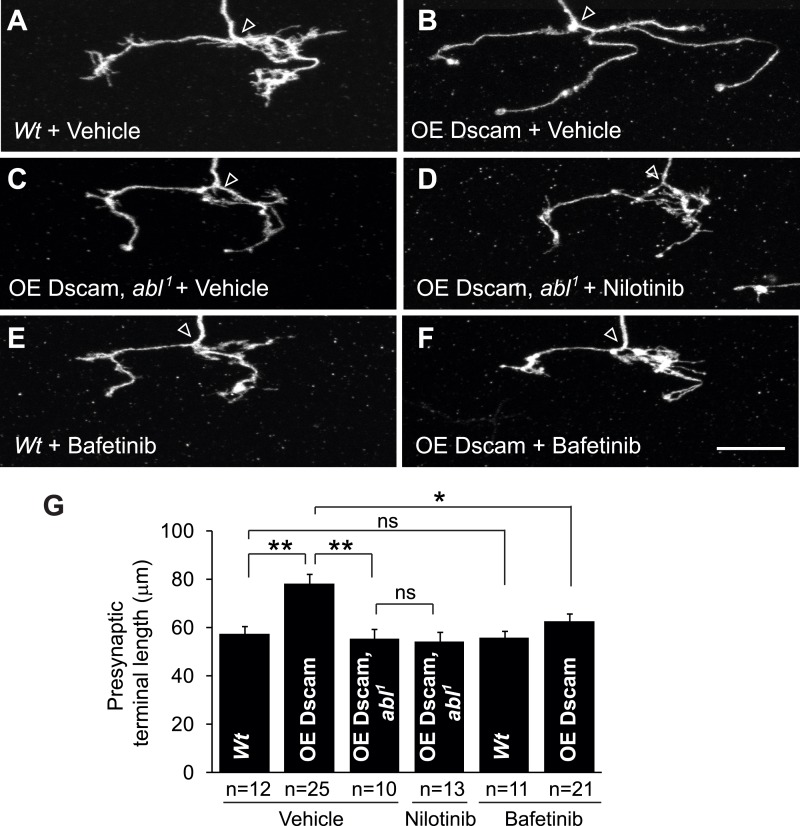
Figure 4. Pharmacological inhibition of Abl mitigates the neuronal defects caused by increased Dscam expression in vivo.
(A) Nilotinib inhibits Drosophila Abl kinase. S2 cells were transfected with either Myc-vector or Abl::Myc, and then treated with either vehicle (DMSO) or 5 μM nilotinib for 6 hr. Total lysates were subjected to western blot analysis with phospho-Y412-Abl (p-Abl) (top) and Myc antibodies (bottom). (B) Quantification of the presynaptic terminal length of the indicated genotypes and drug treatment. Sample number is shown inside each bar. (C–H) Nilotinib treatment mitigates presynaptic arbor enlargement caused by Dscam overexpression (OE Dscam, D and E) and by dFMRP mutations (dFMRPΔ50M, G and H). Nilotinib treatment alone does not affect presynaptic terminal growth (F). The arrowhead in each panel points to the location where an axon elaborates the presynaptic terminal arbor. The MARCM technique was used to generate and visualize single presynaptic terminals of mutant C4da neurons. Drosophila larvae were raised in the presence of either 380 μM nilotinib or vehicle (DMSO) for 4 days before the analysis. Scale bar is 10 μm.