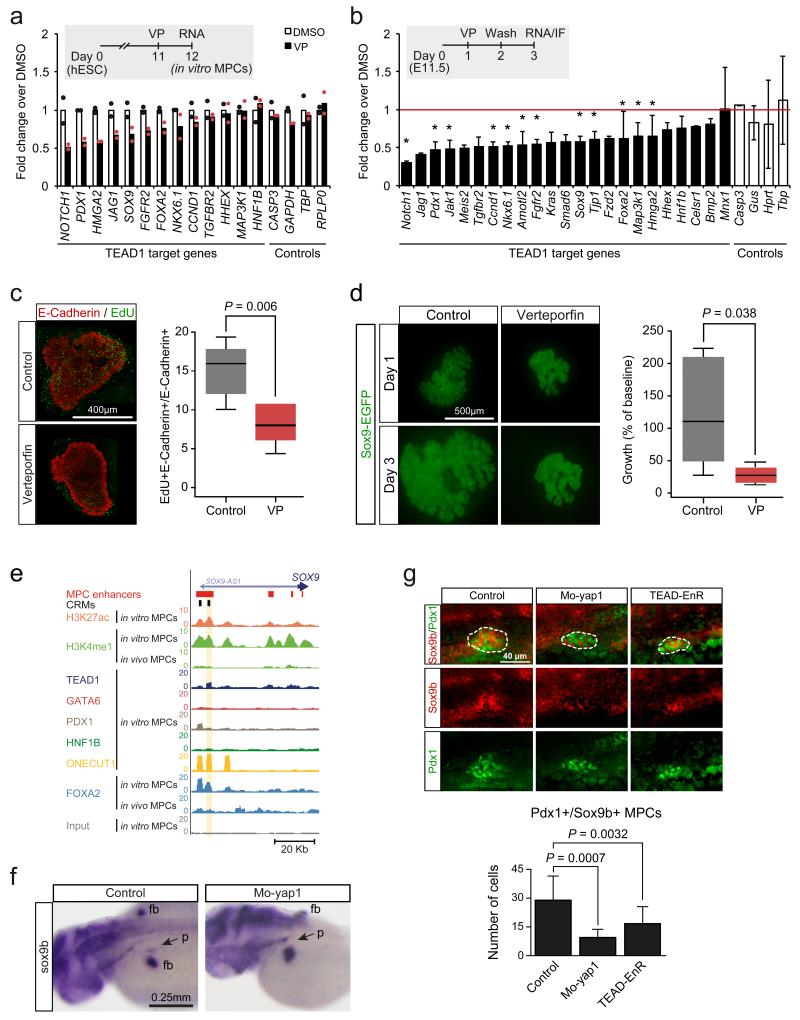
Figure 7.
TEAD and YAP regulation of pancreas development. (a) Human in vitro MPCs were incubated with VP 24 hours to disrupt TEAD-YAP interactions, causing downregulation of genes associated with TEAD1-bound enhancers. Data was normalized by PBGD. Bars show mean values from 2 independent experiments, and points represent mean of 2 technical replicates. (b-d) VP treatment of E11.5 mouse pancreatic explants downregulated orthologs of TEAD1-bound genes, inhibited proliferation and reduced growth of pancreatic epithelial cells. Explants were treated with VP for 24 hours, washed, and incubated 24 hours before analysis. Data was normalized to Gapdh. *Two-tailed t test P<0.05 (individual values listed in Supplementary Table 22). Error bars represent SD from 3 independent experiments (each with n=2-4 embryos/condition). In (c) the percentage of proliferating epithelial cells was quantified with E-Cadherin and EdU immunolocalization. Two-tailed Mann-Whitney P value is shown for 3 experiments (each with n=2-3 pancreas/condition). In (d) GFP+ area in Sox9-EGFP transgenic embryo explants is shown at day 3 compared to day 1. Two-tailed Mann-Whitney test P values are shown for 3 experiments (each with n=2-4 buds/condition). In (c) and (d) boxes are IQR and median, whiskers 1.5 × IQR or extreme values. (e) Snapshot of the human SOX9 locus, encoding a regulator of MPC growth14. The CRM tested in functional assays in Figure 5c and Figure 7f is highlighted. (f) yap1 inhibition decreased pancreatic sox9b expression. Injection of Mo-yap1 caused a reduction or absence of sox9b mRNA in the pancreatic domain (arrow) in 50/102 48 hpf embryos. Control embryos showed pancreatic sox9b expression in 100/100 embryos (Chi-squared P 2.61×10−15). Note that control and morphant embryos always showed sox9b expression in fin buds (fb). (g) Injection of Mo-yap1 (n=10 embryos) or the TEAD-EnR dominant negative (n=12 embryos) caused a decreased number of sox9b+/Pdx1+ pancreatic progenitors (dotted lines) in 24 hpf embryos vs. controls (n=9 embryos). Sox9b was detected by in situ hybridization and Pdx1 by immunofluorescence. The graph reflects the total number of pancreatic progenitors in each embryo. Mo-yap1 also increased ectopic expression of pancreatic markers (Supplementary Figure 7b). Student’s t test P values and SD are shown.