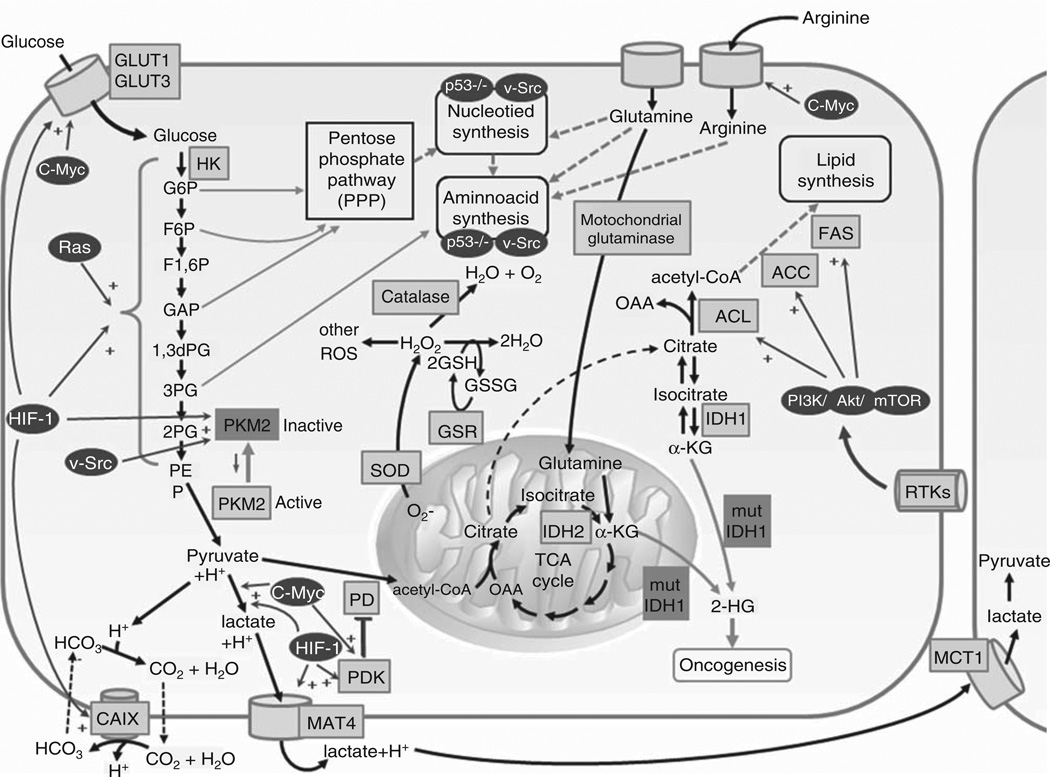
Figure 1. Metabolic pathways and oncogenic signaling in tumor cells.
Malignant transformation is associated with derangements of major metabolic pathways, including glycolysis, mitochondrial metabolism, amino acid metabolism, and fatty acid synthesis.
1,3 dPG: 1,3-biphosphoglyceric acid; 2-HG: 2-hydroxyglutarate; 2PG: 2-phosphoglyceric acid; 3PG: 3-phosphoglyceric acid; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACL: ATP citrate lyase; CAIX: Carbonic anhydrase IX; CoA: Coenzyme A; F1,6P: Fructose 1,6-phosphate; F6P: Fructose 6-phosphate; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; G6P: Glucose 6-phosphate; GAP: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; GLUT: Glucose transporter proteins; GSH: Reduced glutathione; GSR: Glutathione reductase; GSSG: Glutathi-one disulfide; HIF-1: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; HK: Hexokinase; IDH1: Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; IDH2: Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2; MCT1: Lactate transporter; MCT4: Monocarboxylate transporter 4; OAA: Oxaloacetic acid; PD: Pyruvate dehydrogenase; PDK: Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; PEP: Phosphoenolpyruvic acid; PKM2: Pyruvate kinase isozyme 2; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid cycle; α-KG: α-ketoglutarate.