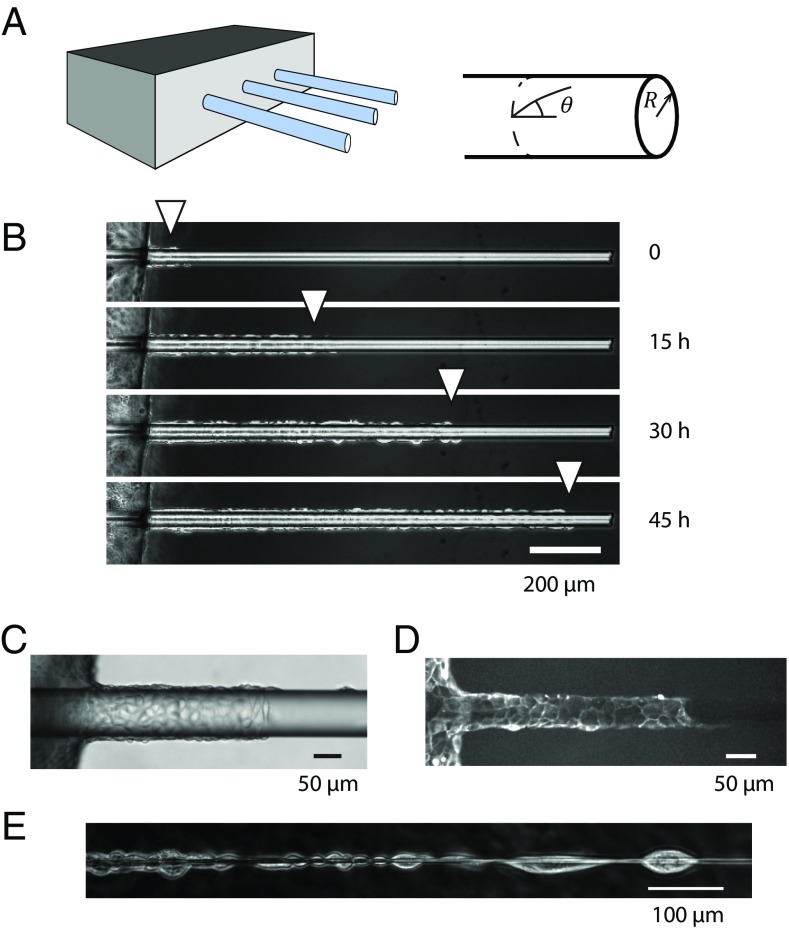
Fig. 1.
(A) Schematic of the experimental device with the glass wires aligned on the edge of a PDMS support. (B) The cells grow to confluence on the support at the left of the pictures before invading the wire collectively (R = 20 µm) (C and D) Phase contrast (C) and fluorescence image (D) of cells migrating on wires (distinct experiments, R ≈ 50 µm). (E) For small radii (R < 5 µm), there is room for one cell only around the wire. Cells then arrange in the form of chains of cells. Note that they still adhere together at their front end and back end. (B and E) MDCK wild-type cells; (C and D) MDCK LifeAct cells.