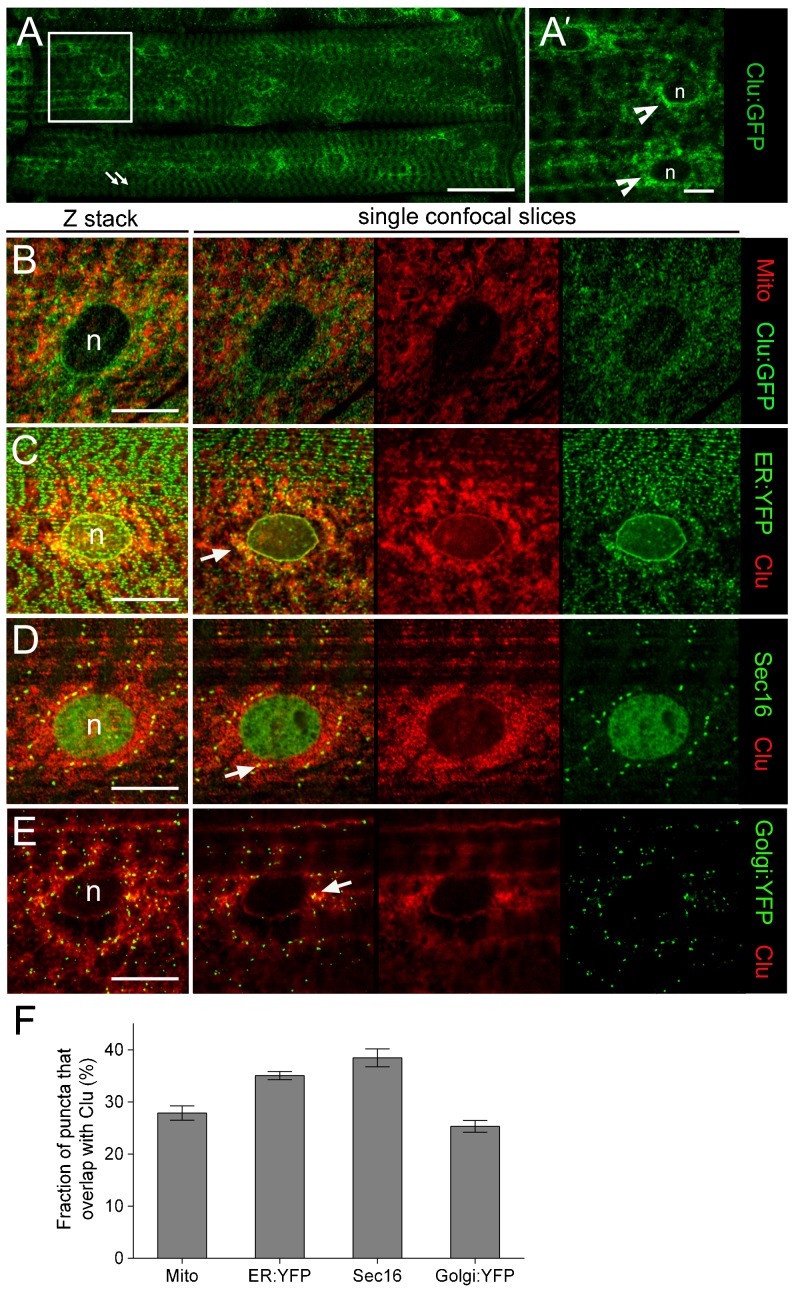
Fig. 2. Clu localizes with dGRASP and Sec16 ER exit sites.
(A–G) Muscle tissue from L3 larvae was dissected and immunostained to examine the subcellular localization of Clu protein. (A,A′) The Clu:GFP protein trap line (green) localizes in a repeated pattern within the muscle (arrows) and accumulates around the nuclei (n; indented arrows). The right panel is a close up of the boxed region in the left panel. (B) The perinuclear accumulation of Clu:GFP (green) reveals little colocalization with mitochondria (red; anti-Complex V). (C–F) An anti-Clu antibody (red) was used to confirm the Clu:GFP nuclear staining pattern and also to discern the localization of Clu puncta with other organelle markers (green) in WT larval muscle. A composite Z-stack is followed by representative single confocal slices. (C,D) Clu-positive puncta overlap with both a general ER marker (C) and the ERES protein Sec16 (D). (E,F) Clu colocalizes with a subset of Golgi:YFP puncta (E). (F) The percentage of puncta of each organelle marker that overlap with Clu protein. Colocalization was determined from multiple single plane images calculated using the Image J JACoP plug-in. Mean±s.e.m. Scale bars, 50 µm (A), 10 µm (A′,B–G).