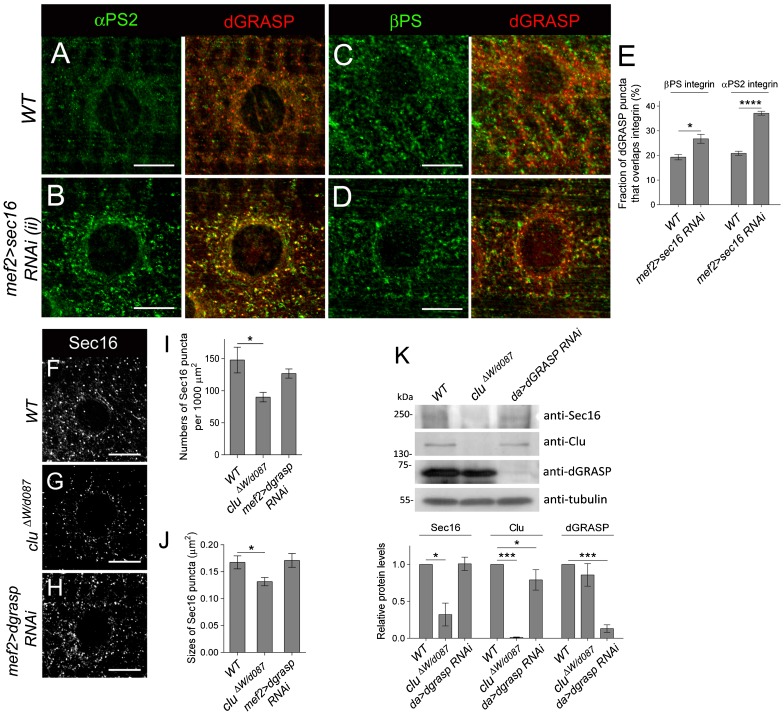
Fig. 6. Sec16 protein levels are reduced in clu mutants.
(A–D) Immunostaining of integrin (green) and dGRASP (red) in L3 contractile muscles. Low amounts of both αPS2 (A) and βPS (C) colocalize with dGRASP around nuclei (n) in WT muscle cells. (B,D) RNAi knockdown of Sec16 in muscle tissues results in the retention of αPS2 in dGRASP-positive puncta (B), while low levels of βPS accumulate around the nuclei (D). (E) Graph depicting the fraction of Sec16 puncta that overlap integrins based upon analysis of multiple images like those presented in panels A–F (*p<0.05; ***p<0.0005). (F–H) Perinuclear staining of Sec16 staining in the indicated genotypes. Sec16 puncta are reduced in clu mutants (G) when compared to WT (F) or dgrasp-depleted muscle tissue (H). (I,J) The number (I) and size (J) of Sec12-positive ERES are reduced in clu mutants. (K) Western blot and band intensity quantification of Sec16, Clu and dGRASP protein levels in the indicated genotypes. Sec16 protein levels are reduced in clu, but not dGRASP mutants (mean±s.e.m.; *p<0.05; ***p<0.005). Scale bars, 10 µm (A–D,F–H).