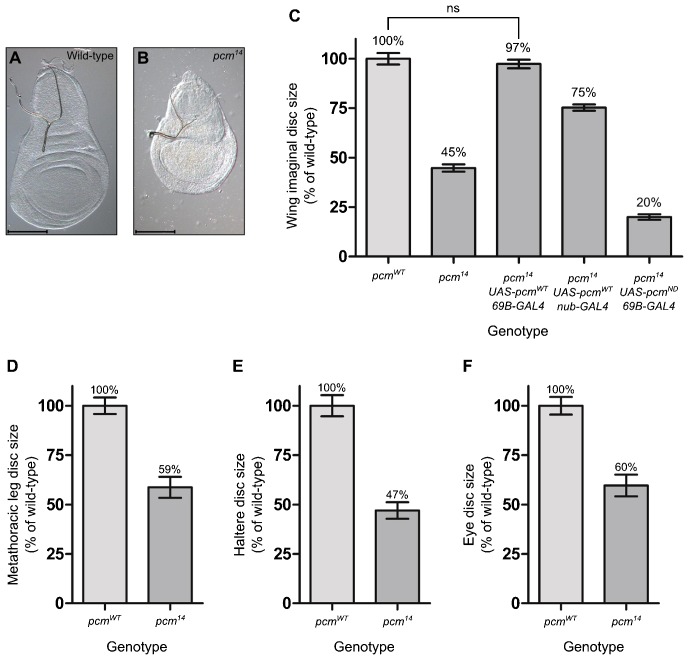
Fig. 3. pcm14 larvae have significantly smaller imaginal discs than wild-type larvae.
(A,B) Representative wild-type and pcm14 wing imaginal discs. Scale bar represents 100 µm. (C) The mean size of pcm14 wing imaginal discs is 45% the size of wild type. This phenotype can be rescued by expressing a UAS-pcmWT construct throughout the wing imaginal disc cells using the 69B-GAL4 driver. Driving UAS-pcmWT expression with nub-GAL4 partially rescues this phenotype to 75% the size of wild type. Expressing a UAS-pcmND construct throughout the disc reduces the mean wing disc size to 20% of wild type (n≥31). (D) The mean size of pcm14 metathoracic leg discs is 59% the size of wild type (n≥21), pcm14 haltere discs (E) are 47% the size of wild-type (n≥21) and pcm14 eye discs (F) are 60% the size of wild type (n≥16). p<0.001 for all comparisons unless indicated, ns = not significant, error bars represent 95% confidence limits.