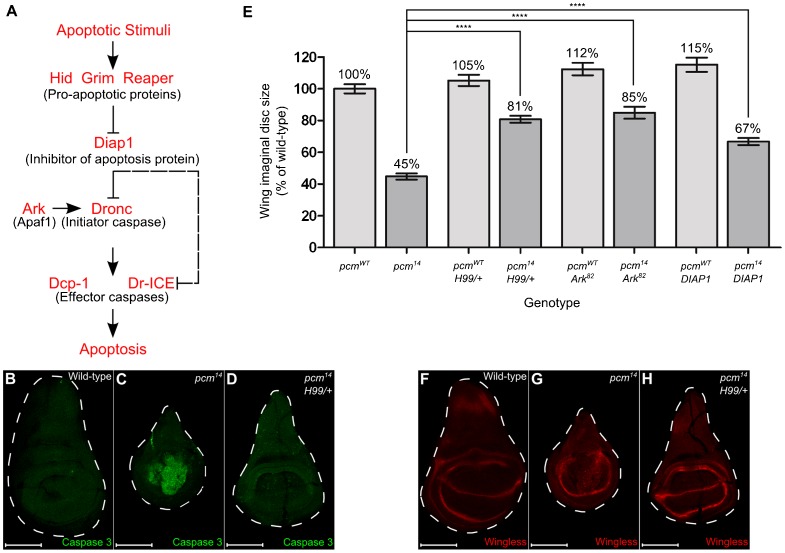
Fig. 7. Inhibiting apoptosis partially rescues pcm14 phenotypes.
(A) A diagrammatic representation of the apoptosis pathway in Drosophila, indicating the main proteins involved in triggering apoptosis in response to an apoptotic stimuli. (B–D) Inhibiting apoptosis in pcm14 wing imaginal discs was achieved by crossing in the Df(3L)H99 deletion (which deletes pro-apoptotic genes hid, grim and reaper) as a heterozygote. The presence of Df(3L)H99 reduced the amount of Caspase 3 staining and increased the size of the pcm14 wing discs (compare C with D) (n = 13). (E) Inhibiting apoptosis partially rescues the size of pcm14 wing imaginal discs. Reducing the copy number of reaper, hid and grim from 2 to 1 using the Df(3L)H99 deletion as a heterozygote (pcm14;;Df(3L)H99/+) rescues the wing disc size from 45% to 81% (n≥31). Use of the Ark82 allele as a homozygote rescues wing disc size from 45% to 85% that of wild type, showing that the adaptor protein Ark is required for much of the pcm14 induced apoptosis (n≥19). Overexpression of the Inhibitor of apoptosis protein DIAP1 using the 69B-GAL4 driver (pcm14;GAL80ts/+;69B-GAL4/UAS-DIAP1) rescues the size of pcm14 discs from 45% to 67% that of wild type, confirming that Pacman is acting through the pathway in A (n≥19) ****p<0.0001. Inhibiting apoptosis in the pcmWT background increases wing disc size to 105% using the Df(3L)H99 deletion (p<0.05), 112% using the Ark82 homozygous mutation (p<0.0001) and 115% using the UAS-DIAP1 (p<0.0001). Error bars represent 95% confidence limits. (F–H) Inhibiting apoptosis rescues the delay in wing imaginal disc development as determined by Wingless staining at 120 hours (compare G with H) (n = 13). Scale bars represent 100 µm.