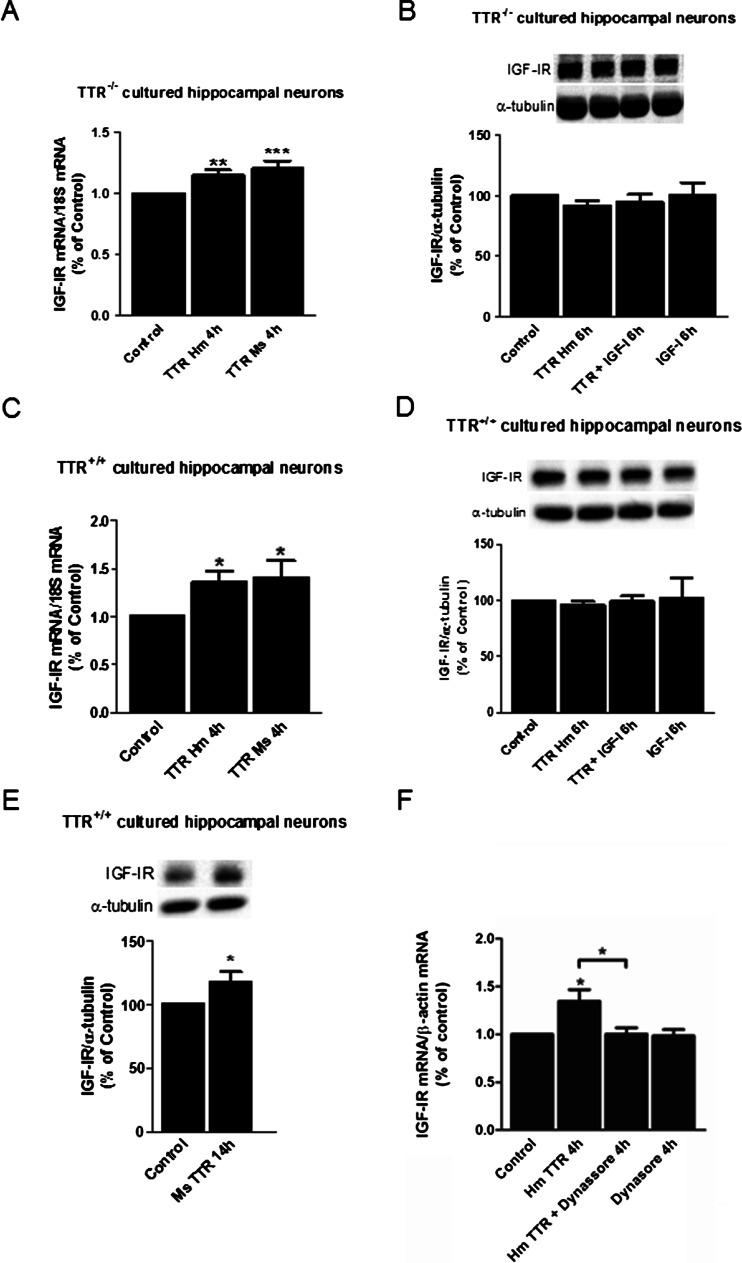
Fig. 4.
TTR regulates IGF-IR mRNA levels in primary cultured hippocampal neurons, from both wild-type and TTR null mice. Cultured hippocampal neurons from TTR null mice (a) and wild-type mice (c) were stimulated with mouse (n = 3) and human transthyretin (n = 4) during 4 h (55 μg/ml), with culture conditioned medium. Total RNA was extracted and IGF-IR and 18S mRNA were semiquantified through real-time PCR. In another set of experiments, cultured hippocampal neurons from TTR null mice (b) and wild-type mice (d) were stimulated with human TTR (n = 3) (55 μg/ml) and/or IGF-I (n = 3) (100 ng/ml) during 6 h, with the culture conditioned medium. IGF-IR and tubulin protein levels were determined by western blot. e Cultured hippocampal neurons from wild-type mice were stimulated with mouse TTR (n = 9) (55 μg/ml) during 14 h, with the culture conditioned medium. IGF-IR and α-tubulin protein levels were determined by Western blot. f TTR regulation of IGF-IR levels in cultured hippocampal neurons is dependent on receptor internalization. Total RNA was extracted and IGF-IR and β-actin mRNA were semiquantified through real-time PCR. Data represents the means ± SEM of four independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, compared with control; **P < 0.01 for the indicated comparison