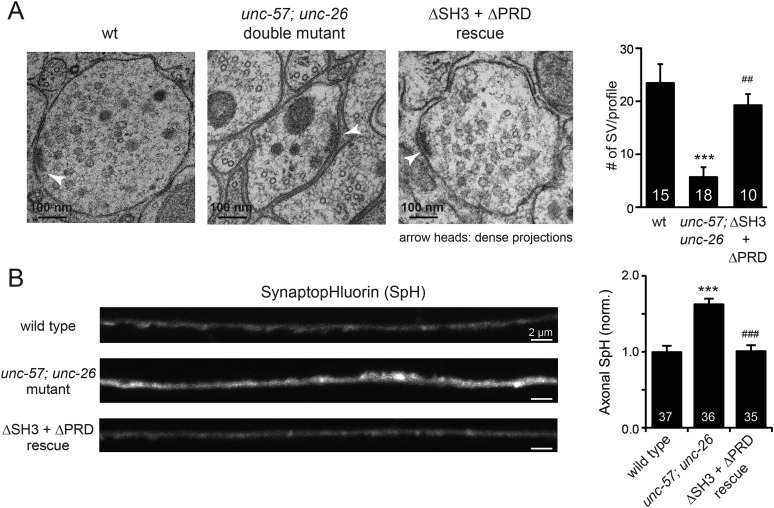
Figure 4. UNC-26∆PRD and UNC-57∆SH3 restore the number of SVs and recover synaptopHluorin retrieval in unc-57; unc-26 double mutants.
(A) Electron microscopy images of neuromuscular junctions were collected from the ventral nerve cords of adult hermaphrodites. Synaptic profiles of 15 synapses of the wt, 18 synapses of the unc-57; unc-26 double mutants, and 10 synapses of the single-copy transgenic UNC-26∆PRD::GFP; UNC-57∆SH3::mCherry animals were analyzed. Arrowheads indicate dense projections. Synaptic vesicle (SV) number was counted in a blind manner. ***, p < 0.0001 when compared to wt controls. ###, p < 0.0001 and ##, p < 0.001 when compared to unc-57; unc-26 double mutants. Scale bar: 100 nm. Error bars indicate SEM. (B) Representative images (left) and summary data (right) for axonal synaptopHluorin (SpH) fluorescence in the dorsal nerve cord are shown for the indicated genotypes. Rescue experiments are done using extrachromosomal arrays carrying Psnb-1::unc-26∆PRD and Prab-3::unc-57∆SH3 (without any fluorescent tags). The number of worms analyzed for each genotype is indicated. ***, p < 0.0001 compared to wt controls. ###, p < 0.0001 when compared to unc-57; unc-26 mutants. Scale bar: 2 µm. Error bars indicate SEM.