Figure 5.
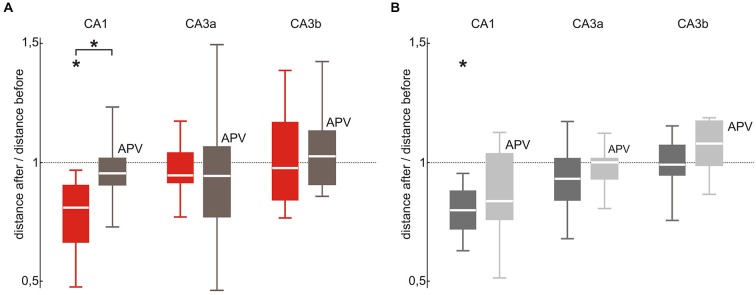
SPW-R stabilization depends on NMDA receptor activation in CA1 but not in CA3. (A) In CA1 the stabilizing effect of repetitive stimulation (red; p < 0.05 n = 8) was abolished by bath application of the NMDA receptor blocker APV (brown; median 0.96, 25th 0.91, 75th 1.0, n = 6, p < 0.05 between both conditions). This difference was absent in the CA3 (CA3a: median 0.95, 25th 0.78, 75th 1.07; CA3b: median 1.03 25th 0.91, 75th 1.14) region. (B) The variability change of spontaneous SPW-R observed after 100 repetitive stimulations in CA1 (dark gray; p < 0.01 n = 10) did not occur under bath application of APV (light gray; CA1: median 0.84, 25th 0.77, 75th 1.05, p = 0.51, n = 8). However, there was no significant different across paradigms. Neither in CA3 repetitive stimulation under bath application of APV altered spontaneous SPW-R variability (CA3a: median 1.0, 25th 0.94, 75th 1.02; CA3b: median 1.08, 25th 0.99, 75th 1.18). “*” means that the finding is significant (p < 0.05).
