Figure 1.
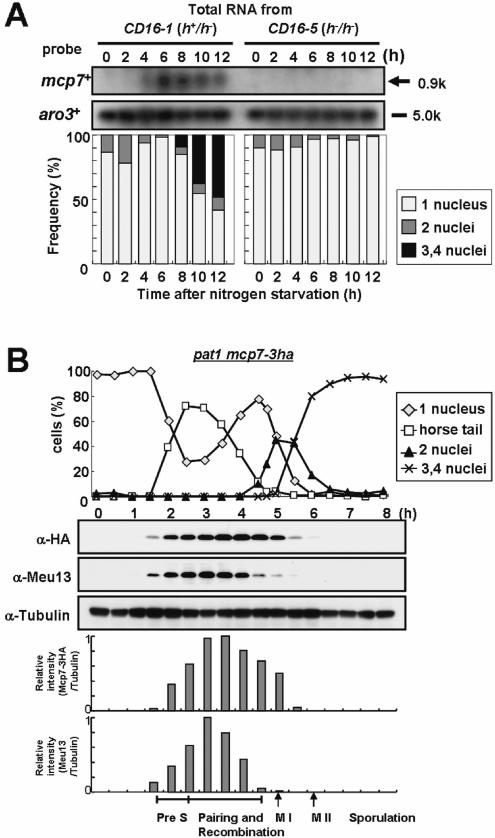
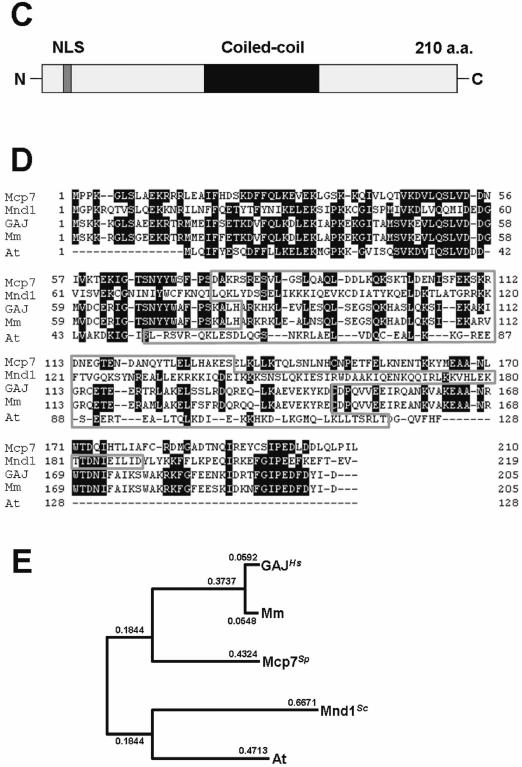
Mcp7 is a meiosis-specific coiled-coil protein that is conserved in a variety of species. (A) Northern blot analysis of mcp7+ and aro3+ (loading control). Total RNA was extracted from CD16-1 (h+/h−) and CD16-5 (h−/h−) cells at the indicated times after meiosis was induced by nitrogen starvation. The RNA was blotted and probed with the ORFs of the mcp7+ and aro3+ genes. The graph below indicates the meiotic profiles of the cells used for RNA extraction. Counting at least 200 cells under a microscope assessed the frequencies of Hoechst33342-stained cells that bear one, two, three or four nuclei. (B) Western blot analysis of the production of the Mcp7–3HA and Meu13 proteins during the synchronous meiosis of strain ST123. The tubulin levels are also examined as a loading control. To quantify the result, the intensities of the bands were measured by a densitometer and the relative values were presented as bar graphs. (C) A schematic presentation of the Mcp7 protein. These motifs were identified by PSORT II (http://psort.nibb.ac.jp/). (D) Multiple sequence alignment of Mcp7 with the orthologous proteins in S.cerevisiae (Mnd1), Homo sapiens (GAJ), M.musculus (Mm) and A.thaliana (At). Gaps inserted in the alignment to attain maximal homology are indicated by hyphens. The amino acids that are identical between three or more of the five species examined are shaded in black. The gray region indicates a predicted coiled-coil motif. (E) The phylogenetic tree of Mcp7. The relationships between the orthologous proteins were inferred by the neighbour-joining method (29). The numbers represent the phylogenetic distance. Both the sequence and phylogenetic analyses were performed by using a GENETYX program (Software Development Co., Ltd).
