Figure 2.
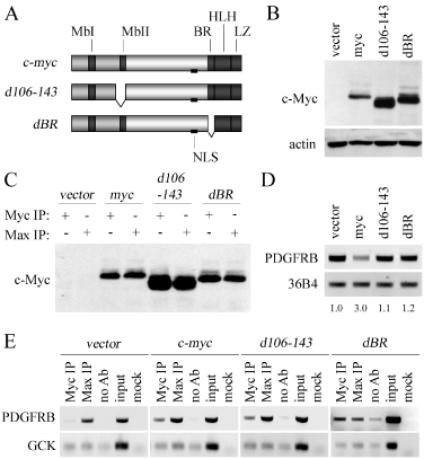
Promoter-binding and gene repression by c-Myc are separable functions. (A) Schematic of the human c-Myc, c-Mycd106-143 (d106-143), and c-MycdBR (dBR) proteins and the domains they contain Myc-homology box 1 (MbI) and 2 (MbII); nuclear localization signal (NLS); basic region (BR); helix–loop–helix (HLH); leucine zipper (LZ). (B) Immunoblot of c-Myc protein (9E10) and actin expression in Rat-1c-myc−/− cells infected with an empty retroviral vector, or retrovirus carrying c-myc, c-mycd106-143 (d106-143), or c-mycdBR (dBR). (C) Immunoblot for c-Myc protein (9E10) following immunoprecipitation (IP) using c-Myc (N-262) or Max (C-124) antibody in the Rat-1c-myc−/− cell lines indicated. (D) Expression of endogenous PDGFRB and control 36B4 in the Rat-1c-myc−/− cell lines indicated, as assessed by RT–PCR. Fold-repression of the normalized PDGFRB transcript level, relative to the Rat-1c-myc−/− vector control cell line, is shown. (E) ChIP using c-Myc or Max antibody in the Rat-1c-myc−/− cell lines indicated were conducted as described in Figure 1D and E.
