Figure 5.
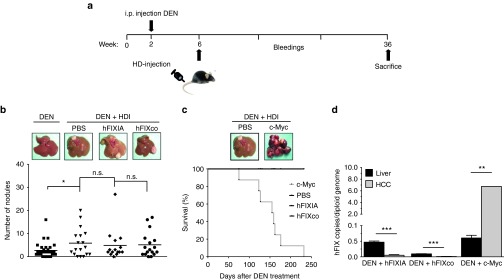
Safety assessment in a tumor-prone hepatocellular carcinoma model. (a) Diagram showing the timeline and experimental procedure. C57BL/6 male mice were subjected to a preweaning protocol of diethylnitrosamine (DEN) initiation. DEN (12.5 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally (i.p) in 14-days-old-mice. 4-weeks later, mice were hydrodynamically transfected with 10 μg PB-hFIXIA or 500 ng PB-hFIXco transposons and 2 μg of mPB-encoding plasmid. hFIX expression was measured on plasma samples collected at different time points (bleedings) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. As controls, mice received PBS injection or a PB-c-Myc transposon (10 μg) 2 μg of mPB-encoding plasmid. Tumor burden was assessed 36-weeks post-DEN initiation. (b) Representative images showing the macroscopic liver appearance 36-weeks post-DEN initiation in mice that received DEN only or DEN in combination with hydrodynamic injection (HDI). Liver nodules were counted for each group. (c) Representative picture showing the macroscopic tumor burden associated with PB mediated c-Myc expression and Kaplan–Meier survival curve of PB-c-Myc transposon and PBS-injected mice (c-Myc, n = 9, median survival 157 days). (d) Transposon copy number quantification from genomic DNA isolated from normal liver biopsy (hFIXIA; n = 15; hFIXco, n = 17; c-Myc, n = 9) and HCC nodules (hFIXIA, n = 30; hFIXco, n = 34; and c-Myc, n = 18). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. n.s. indicates not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
