Figure 6.
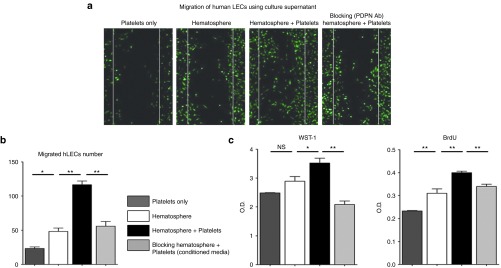
Cocultured supernatant from podoplanin-positive monocytes (PPMs) and platelets enhances the migration, viability, and proliferation of hLECs. (a) Representative figure of hLECs' migration in various conditioned media. hLECs migrated most rapidly in the presence of the conditioned medium from coculture of PPMs and platelets, while migration of hLECs was significantly attenuated when treated with blocking antibody against podoplanin. (b) Bar graph representing the number of the migrating hLECs (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; n = 3 per experiment). (c) Quantitative data showing the viability and proliferation of hLECs under various conditions. hLECs cultured under the conditioned medium from coculture of PPMs and platelets demonstrated greater viability and proliferation compared to the culture medium from monoculture of platelets or PPMs. However, the enhanced capacity of hLECs was attenuated by blocking the podoplanin (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; n = 3 per experiment). BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine; hLECS, human lymphatic endothelial cells; LEC, lymphatic endothelial cells; NS, nonsignificant; O.D., optical density; WST-1, water soluble tetrazolium salts-1.
