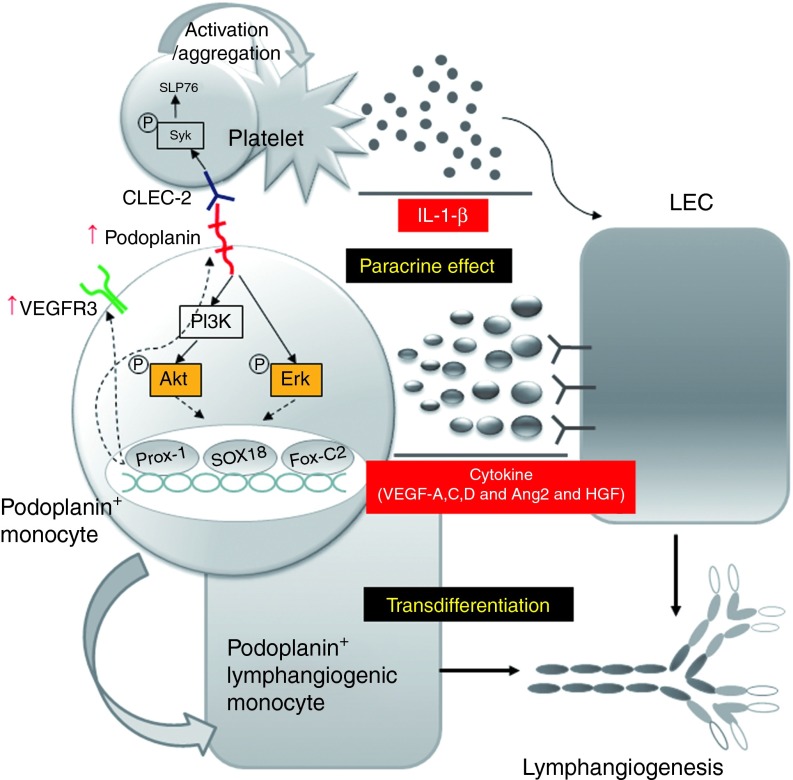
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of lymphangiogenesis by the synergistic interaction between PPMs and platelets through podoplanin/CLEC-2 interaction. When the hematosphere is generated from a suspension culture of human peripheral blood monocytes under high cell density, there is a huge expansion of PPMs in hematospheres for several days. These cells express lymphatic endothelial cell–specific markers, such as Prox-1, Sox-18, FoxC-2, and VEGFR-3. When podoplanin on these monocytes is stimulated by CLEC-2 on platelets, the interaction of CLEC-2 on platelets and podoplanin on monocytes turns on Akt or Erk signaling pathways that provoke two changes on monocytes: (i) the enhanced expression of Prox-1, Sox-18, FoxC-2, and VEGFR-3 and the transdifferentiation to lymphatic endothelial cells and (ii) the enhanced secretion of lymphangiogenic cytokines, such as VEGF-A,C,D, angiopoietin-2, and HGF. Meanwhile, the interaction of CLEC-2 on platelets and podoplanin on monocytes stimulates platelets, leading to morphologic changes and secretion of lymphangiogenic cytokine, IL-1-β. Overall, these interactions facilitate lymphatic neovascularization and augment wound healing. CLEC-2, C-type lectin–like receptor-2; IL, interleukin; LEC, lymphatic endothelial cells; PPMs, podoplanin-positive monocytes; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.