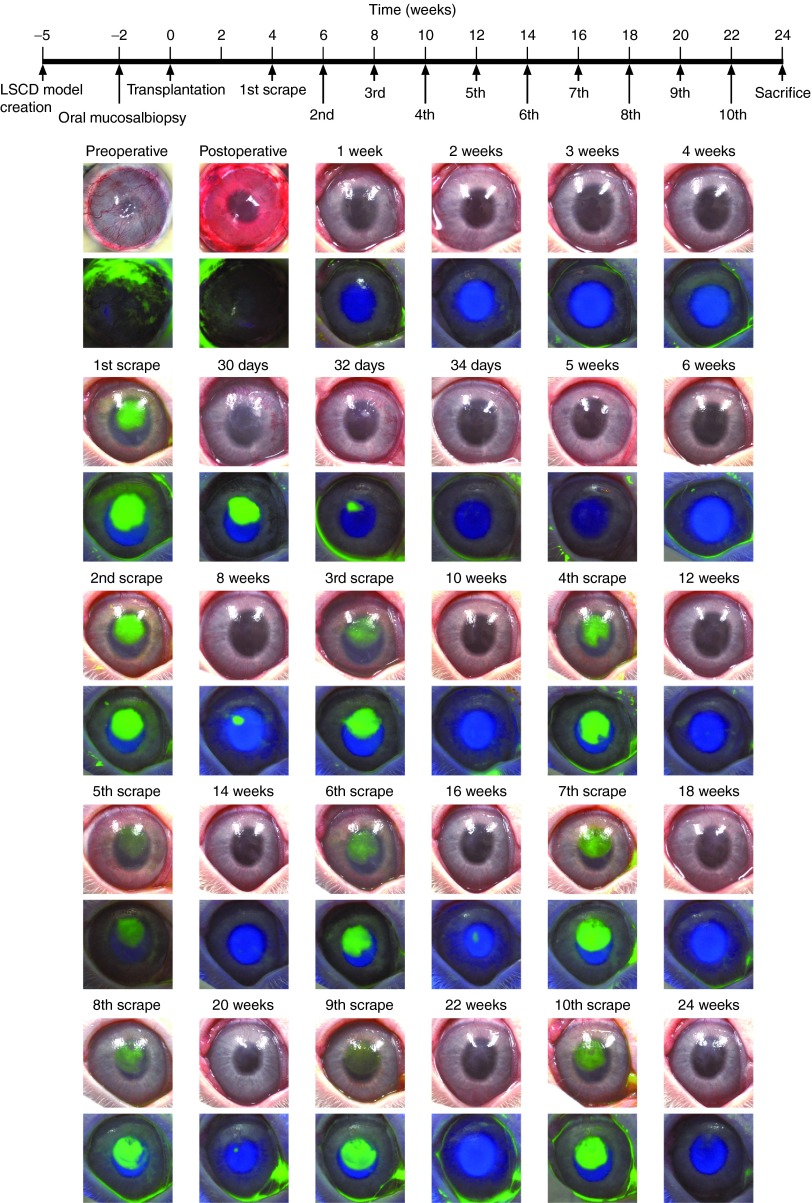
Figure 3.
Repeated wound-healing assay of proliferative and differentiation potential of transplanted oral mucosal epithelial cell (OEC) sheets. Neovascularization and opacification were observed in the rabbit limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD) model 5 weeks after the surgery. An OEC sheet was transplanted onto the ocular surface after the removal of pannus without defects. Ocular surface was then reconstructed and confirmed to remain clear for 4 weeks, and then, the center of transplanted corneal surface was scraped to create a wound. Fluorescein staining revealed that the corneal stroma was completely reexposed. Proliferating epithelial cells covered the scraped area within a few days allowing the ocular surface to recover which was then confirmed to be stable with no evidence of fluorescein staining. Two weeks after the first scraping, the central part of healed ocular surface was physically scraped again. Epithelial cells migrated and covered the scraped area again after the second scraping. Similarly, the transplanted OEC sheet ocular surface was scraped every 2 weeks to a total of 10 times, and reepithelialization was observed after every scraping.