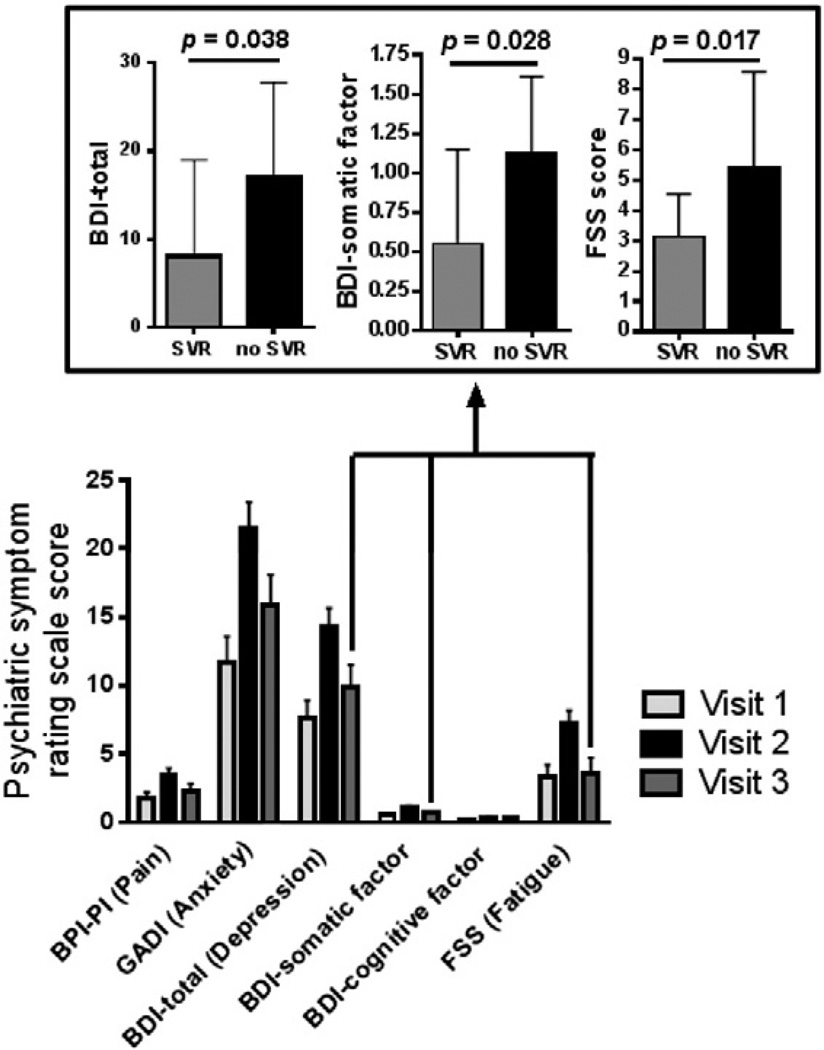
Fig. 1.
Psychiatric symptom rating scale scores before, during and after interferon alpha-based antiviral therapy (IFN) for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (IFN+ Group, n = 33). Significant (p < 0.05) changes across visits were observed on the Beck Depression Inventory, Second Edition (BDI) Total, BDI Somatic Factor, BDI Cognitive Affective Factor, Generalized Anxiety Disorder Inventory (GADI), Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS), and Brief Pain Inventory-Pain Interference (BPI-PI); specifically, psychiatric symptoms increased at Visit 2 during IFN and then returned to near baseline levels at Visit 3 following IFN termination. Inset box illustrates that for individuals undergoing IFN for HCV (IFN+ Group), there were significant effects of sustained viral response (SVR) on fatigue (FSS), overall depression (BDI Total), and somatic depression (BDI Somatic Factor) scores. Participants who achieved an SVR (n= 19) reported less fatigue (p= 0.017), less overall depression (p = 0.038), and fewer somatic depressive symptoms (p = 0.028), as compared with those who did not achieve an SVR (n= 6).