Figure 2. HCMV UL37 proteins.
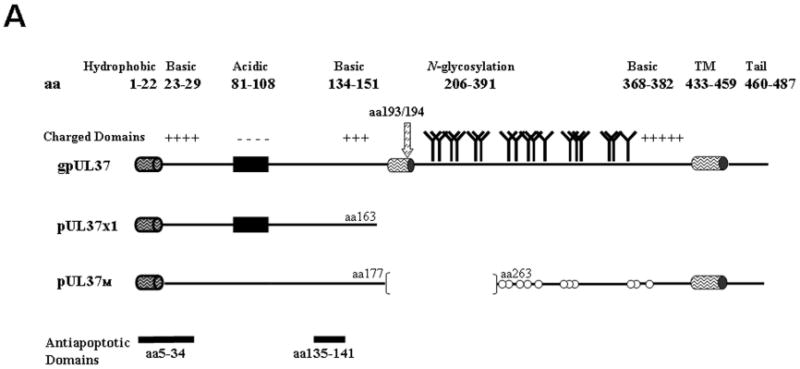
A. Schematic representation of the predominant UL37 protein isoforms. The bipartite leader sequence is shared by all UL37 isoforms and is comprised of a hydrophobic domain (cylinder, aa 1 to 22) and downstream residues (aa 23 to 34). Internal TM domain (cylinder, aa 178 to 196), internal signal peptidase I cleavage site (arrow, aa 193/194), consensus N-glycosylation sites, and C-terminal TM domain (aa 433 to 459) are indicated for gpUL37. Elements common to multiple UL37 isoforms are repeated in each protein. Consensus N-glycosylation sites for pUL37M are marked by open circles to denote that they are not used, as this isoform lacks an internal TM domain needed to direct downstream sequences into the ER lumen. The two anti-apoptotic domains (aa 5 to 34 and 135 to 141), present in all three isoforms, are highlighted at the bottom of the figure.
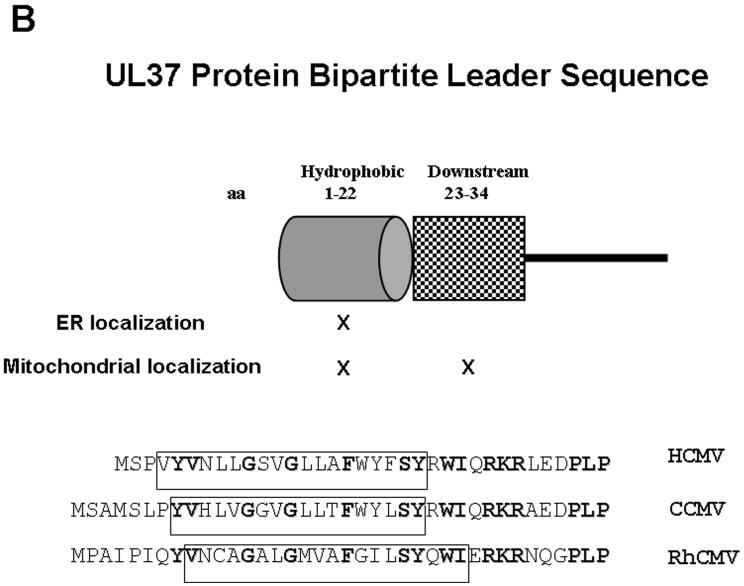
B. Cartoon representation of the pUL37x1\vMIA N-terminal bipartite leader sequence, highlighting the sequences needed for ER and mitochondrial importation [71]. The lower panel displays the sequence similarities in pUL37x1\vMIA leader sequences of HCMV (Accession number=ABV71569), CCMV (Accession number=AAM00687), and rhesus monkey CMV (Accession number=AAZ80560). Bolded residues are strictly conserved, while those boxed show regions of alpha helical structure (predicted by HMMTOP).
