Fig. 2.
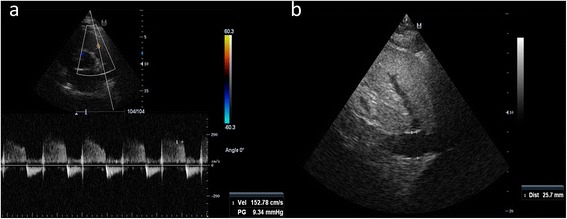
Example for estimating the pulmonary artery diastolic pressure (PAdP). a. The end-diastolic velocity of the pulmonary regurgitation jet was measured (parasternal short-axis view) and pressure gradient was automatically calculated (9.34 mmHg). b. Right atrial pressure was estimated in 15 mmHg through the analysis of size (dilated, 25.7 mm) and collapsibility (diminished) of the inferior vena cava. PAdP is obtained as the sum of 9.34 and 15 mmHg, resulting in a highly elevated PAdP (equivalent to an elevated left atrial pressure), of 24.3 mmHg
