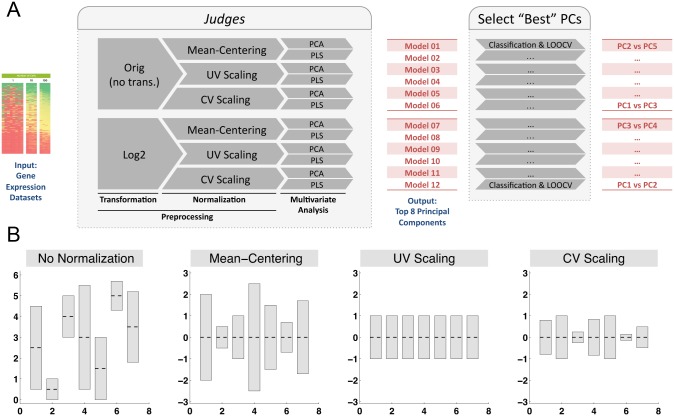
Fig 1. Schematic of multiplexed component analysis (MCA) algorithm for evaluating gene expression datasets.
(A) Since there is no prior information on how the changes in gene expressions affect the immune response during acute SIV infection, we use an array of mathematical techniques to be able to observe the data from different viewpoints. A “judge” is defined as the combination of a transformation, a normalization technique and a multivariate analysis method. Each dataset is analyzed by 12 different judges, forming a Multiplexed Component Analysis (MCA). Each judge provides a model consisting of a set of principal components (PCs), which are used to classify datasets based on one of the two output variables: time since infection or SIV RNA in plasma (classification schemes). For each judge, the two PCs that provide the most accurate and robust classification are chosen for further analysis. (B) Normalization methods include mean-centering (MC), unit-variance scaling (UV), and coefficient of variation scaling (CV); each method results in a different representation of the data, emphasizing different characteristics of the original data set. The MC normalization method emphasizes the genes with the highest absolute variations; the UV normalization method gives equal weight to each gene in the dataset; the CV normalization method emphasizes the genes with the highest relative changes.