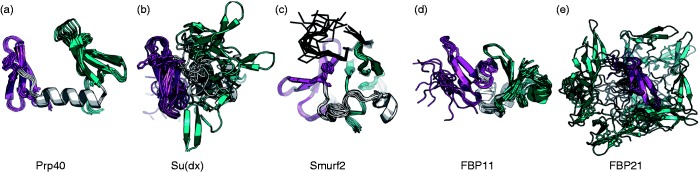
Figure 3.
Structures of tandem WW domains reveal a wide range of interdomain flexibility. A range of mobility between WW domains is observed in different solved tandem domain structures. (a) Yeast splicing factor Prp40 WW1–WW2 [Protein Data Bank (PDB54) id 1o6w45]. (b) E3 Ubiquitin ligase Su(dx) WW3–WW4 (PDB id 1tk746). (c) E3 Ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 WW3–WW4 bound to its peptide ligand (PDB id 2kxq33). (d) Human Prp40 homologs FBP11 (PDB id 2l5f) and (e) FBP21 (PDB id 2jxw40). The first WW domain, linker, and second WW domains are shown on the left in pink, in light gray, and to the right in cyan, respectively. The peptide is displayed as black trace (in (c)). Slight reorientations were performed to optimally display flexibility (in FBP21, the first domain is located in the center, in front of the rest). See text for more details. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)