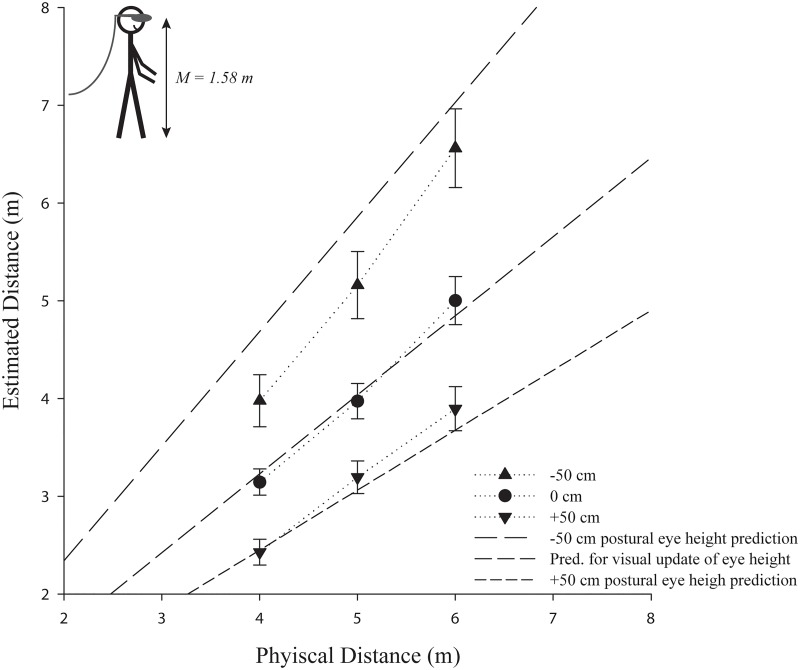
Fig 5. The effect of a manipulated virtual eye height (-50 cm or +50 cm) on egocentric distances in a standing position in comparison to the respective baseline condition (0 cm).
Error bars represent ±1 SE. The actual mean participant (postural) eye height in the experiment is depicted in the left upper corner. Note: (a) The predictions are shifted by the observed underestimation in the baseline condition to account for the usually observed distance underestimation in head mounted displays (in an ideal world, the 0 cm estimates would correspond to veridical performance). (b) If the virtual eye height were used, there should be no differences and the prediction for visual eye height would apply for all conditions.