Figure 3.
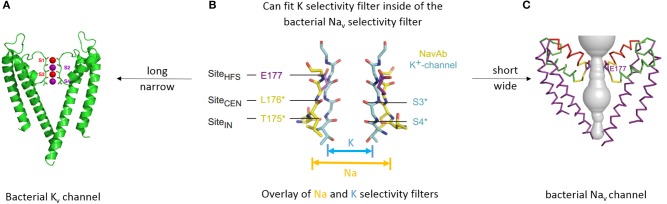
Different structures underlying different mechanisms of selectivity in potassium and sodium channels. (A) X-ray structure of bacterial KcsA potassium channel (A) (Doyle et al., 1998). Only two subunits are shown for clarity. Backbone carbonyls in the selectivity filter are red. Potassium ions (purple spheres) occupy two of the four sites (s2 and s4). Water molecules (red spheres) are shown in positions s1 and s3. (B) Overlay of the selectivity filter regions in KcsA and NavAb. NavAb (yellow carbons) has a shorter and wider pore in the selectivity-filter region. (C) X-ray structure of bacterial sodium channel NavAb (Payandeh et al., 2011). P2 helices are red and high field strength site glutamate residues (E177) are purple. (B,C) are reproduced from Payandeh et al. (2011), with permission.
