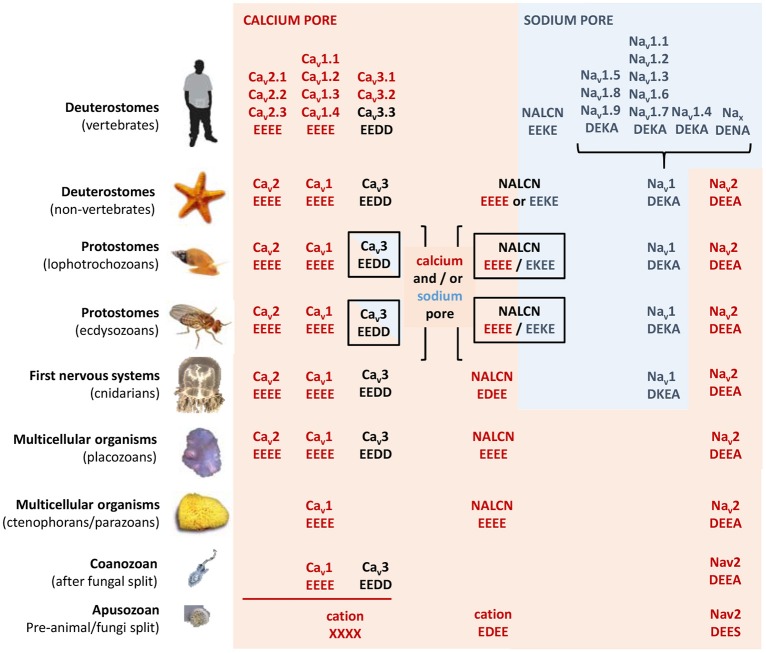
Figure 5.
Evolution of calcium and sodium HFS sites in 4x6TM channels. Most basal metazoan species have only calcium-selective pores: Cav1 (EEEE), Cav2 (EEEE), Nav2 (DEEA), and NALCN (EEEE). Sodium selective HFS sites contain a lysine residue (the DEKA ring) in most animal groups. Exceptions are the simplest animals with sodium-dependent action potentials (cnidarians) that have a DKEA HFS site (Anderson et al., 1993; Spafford et al., 1998). Dual sodium and calcium selectivity in NALCN is due to alternative splicing at HFS site with exon 15 or exon 31 (Senatore et al., 2013). T-Type calcium channels with mixed sodium and calcium selectivities have a shorter extracellular loop with three cysteines or a longer loop with five cysteines in Domain II coded by exons 12a and 12b, respectively (Senatore et al., 2014a). Vertebrates have sodium-selective channels. They lack calcium-selective Nav2 channels and the NALCN splice isoform with the calcium selectivity filter (EEEE). Vertebrates also lack sodium-selective T-Type channels as found in the invertebrate heart.