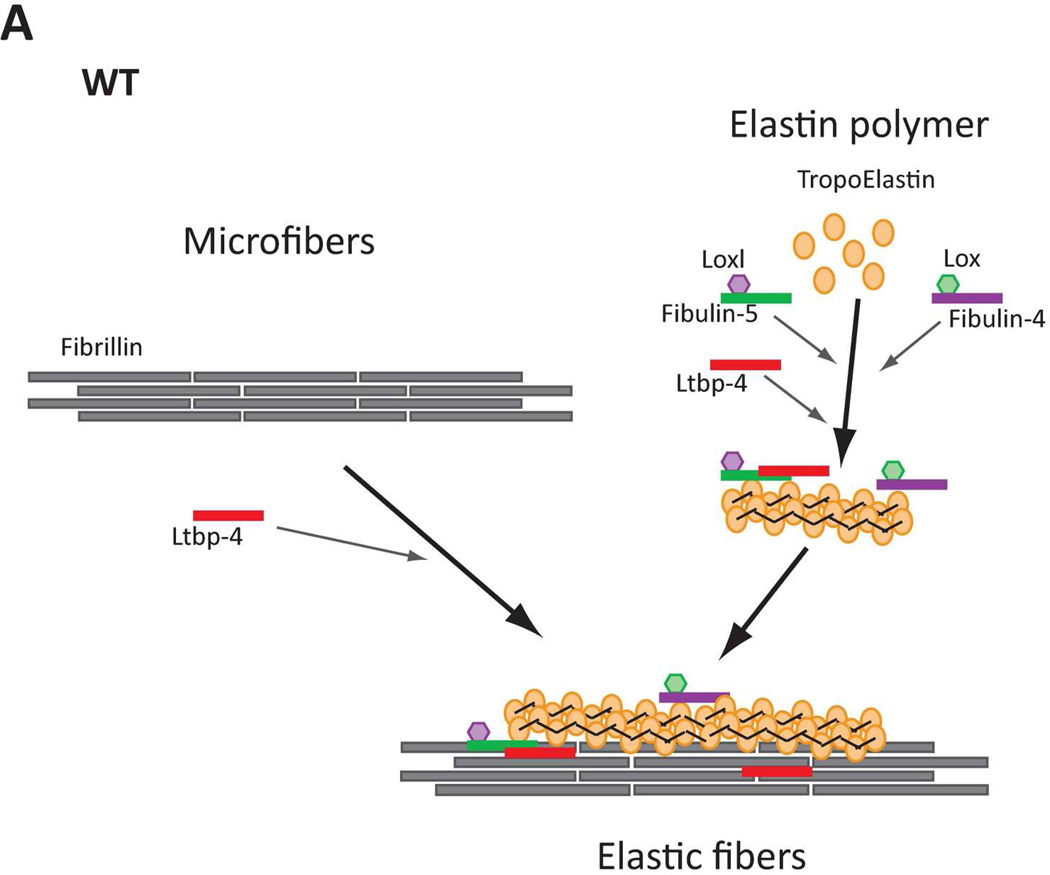
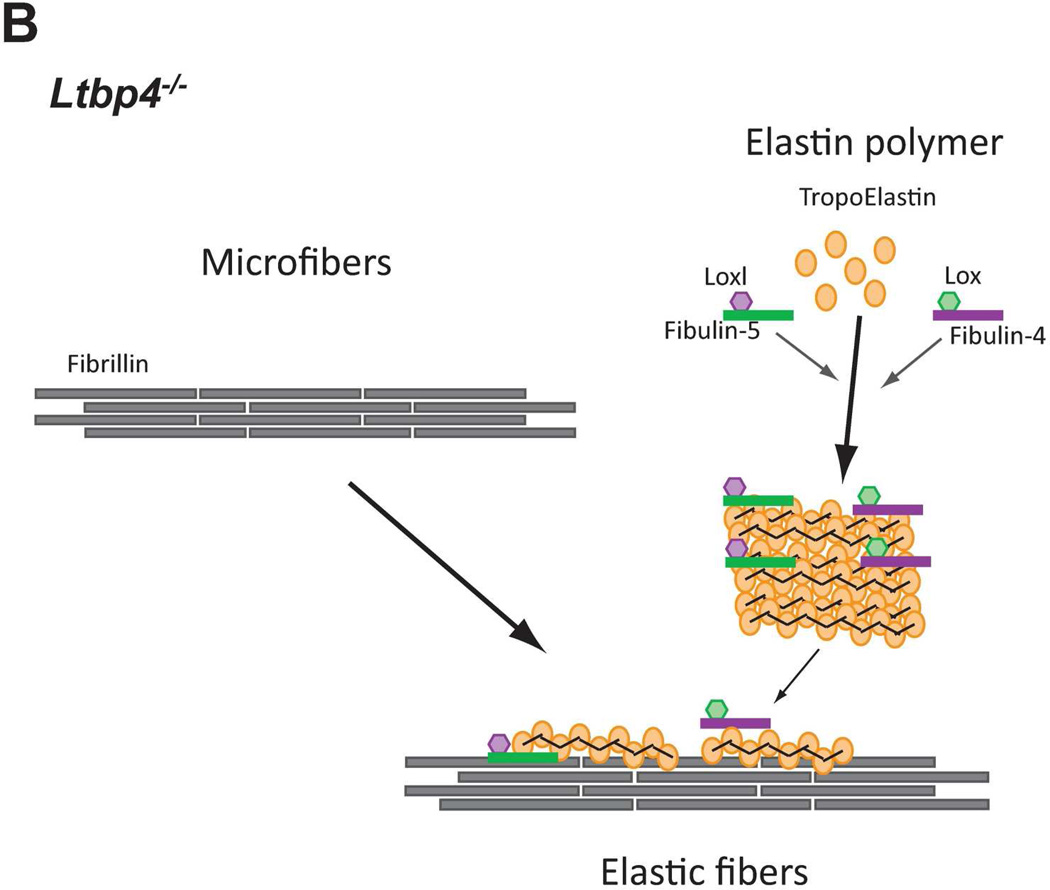
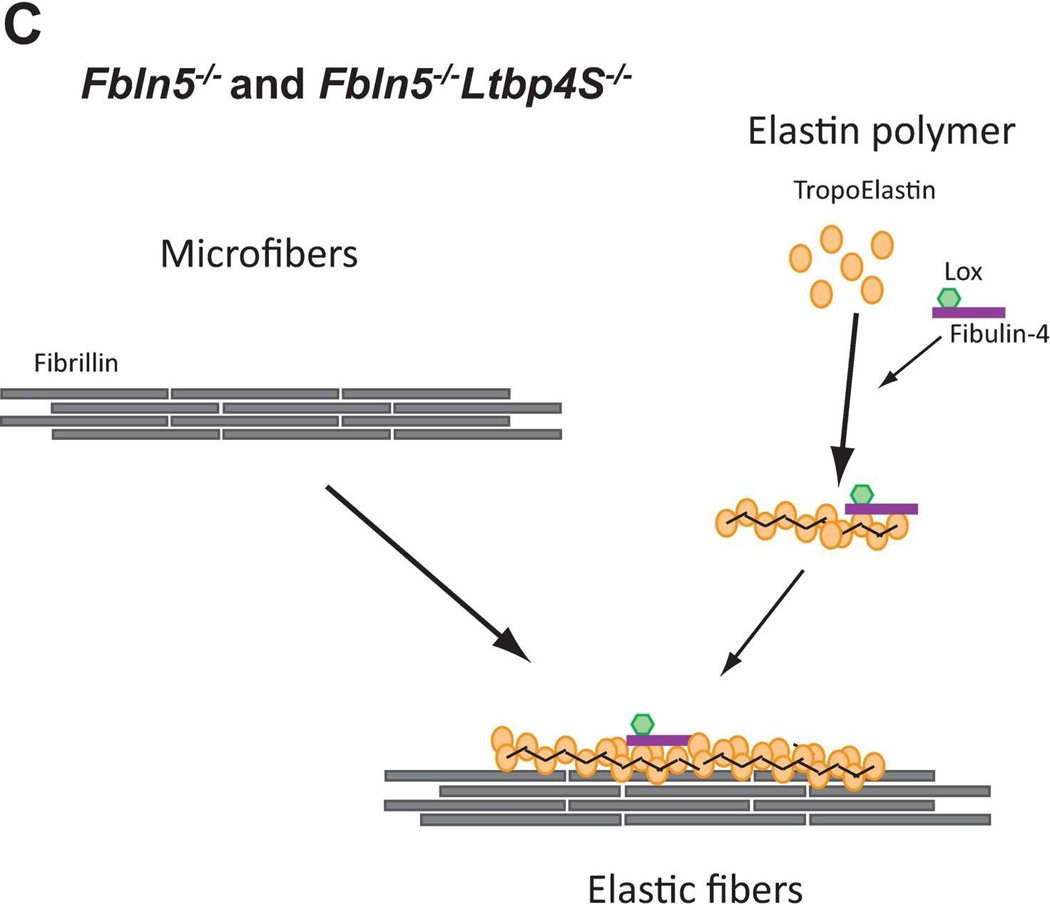
Figure 8.
Models of elastic fiber assembly in Ltbp4S−/− and Fbln5−/−;Ltbp4S−/− lungs. A. Normal Lungs. In normal (WT) lungs elastic fiber assembly requires self-assembly of fibrillin molecules into microfibers as well as secretion and micropolymerization of tropoelastin molecules. Elastin polymerization is catalyzed by lysyl oxidase (LOX) or lysyl oxidase like-1 (LOXL-1) enzymes. LOX interacts with fibullin-4, whereas LOXL-1 interacts with fibulin-5. LTBP-4 interacts with both fibrillin and fibulin-5 and promotes elastogenesis. B. Ltbp4S−/− Lungs. In Ltbp4S−/− lungs self-assembly of fibrillin is not affected and there is normal formation of microfibers. However, large elastin aggregates form, as there is no carrier protein to target fibulin-5-elastin complexes to or along microfibers. Only a small fraction of elastin is integrated into the microfibers, presumably through the direct interaction of fibulin-4 and fibulin-5 with fibrillin-1. C. Fbln5−/−;Ltbp4S−/− and Fbln5−/− lungs. In Fbln5−/−;Ltbp4S−/− as in Fbln5−/− lungs, the large elastin aggregates do not form, because there is no initial accumulation of fibulin-5-elastin complexes. Elastogenesis occur through an alternative pathway presumably involving the integration of fibulin-4-elastin complexes into microfibrillar scaffolds rather than the integration of LTBP-4-fibulin-5-elastin complexes into microfibers.