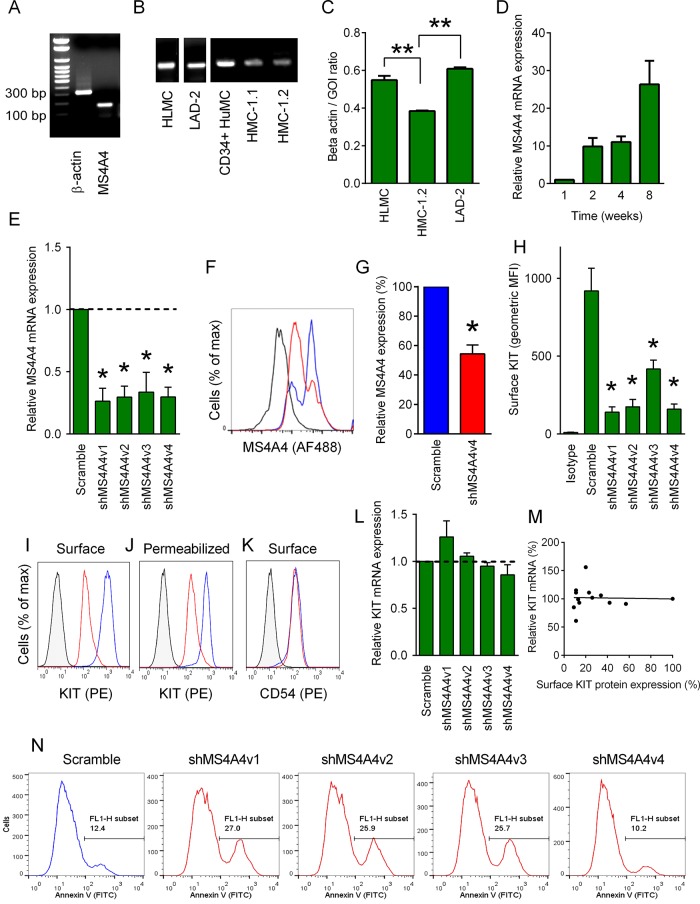
FIGURE 1:
MS4A4 in human MC promotes surface KIT receptor expression. (A) RT-PCR for MS4A4 and β-actin in HLMCs. (B) All human MC types tested expressed MS4A4 mRNA. (C) qRT-PCR for MS4A4 mRNA in human MCs. Data calculated as the ratio of MS4A4 compared with β-actin for each sample (n = 3–11). (D) qRT-PCR for MS4A4 mRNA in CD34+-derived peripheral blood MC over time during culture (n = 3). (E) qRT-PCR for MS4A4 mRNA in LAD-2 cells using four shRNA constructs targeting MS4A4 (n = 5). (F) Flow cytometry histogram of total MS4A4 protein expression in LAD-2 cells treated with scrambled shRNA control or the shMS4A4v4 construct (isotype, black; scramble, blue; shMS4A4v4, red). (G) Mean flow cytometry data for MS4A4 expression calculated from the geometric MFI and expressed as percentage of scramble control (n = 4). (H) Mean flow cytometry data for surface KIT expression in shMS4A4-transduced LAD-2 cells (n = 4). (I) Flow cytometry histogram of surface KIT expression. (J) Flow cytometry histogram of total KIT expression in permeabilized cells. (K) Flow cytometry histogram of surface CD54 expression. (L) qRT-PCR for KIT mRNA with shMS4A4 constructs. Values are relative expression compared with scramble control (n = 3). (M) Correlation between surface KIT protein expression and relative KIT mRNA expression calculated as relative percentage compared with scramble control. (N) Flow cytometry histograms of annexin V staining from LAD-2 cells transduced with either control shRNA or shMS4A4 constructs at day 7 postinfection. Data are mean + SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001.