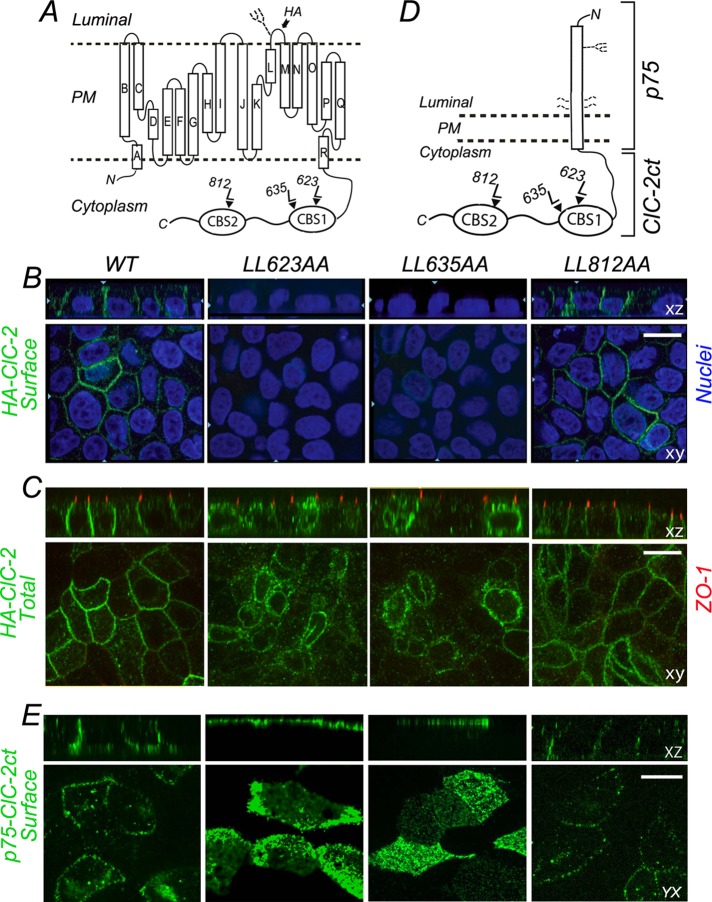
FIGURE 2:
Basolateral localization of ClC-2 is disrupted by L → A mutagenesis of ESMI623LL or QVVA635LL. (A) Cartoon representation of HA-tagged ClC-2. The HA epitope is located in the short luminal loop between L and M α-helices; this loop contains an N-linked glycan. Note the CBS1 and CBS2 domains in the C-terminus that house the three dileucine motifs. (B) Stable MDCK cell lines expressing WT or mutant HA-ClC-2 with alanine replacements of dileucine pairs for each individual dileucine motif, HA-ClC-2[623LL/AA], HA-ClC-2[635LL/AA], and HA-ClC-2[812LL/AA]. Cells were polarized after 4 d and cultured on Transwell filters and immunolabeled with HA antibody before permeabilization to decorate surface ClC-2 (green). Note the basolateral localization of HA-ClC-2[WT] and HA-ClC-2[812LL/AA]; in contrast, HA-ClC-2[623LL/AA] and HA-ClC-2[635LL/AA] are not expressed at the cell surface. (C) The same cell lines shown in B were decorated with HA antibodies after cell permeabilization; tight junctions are labeled with anti-ZO1 (red). Note the intracellular accumulation of HA-ClC-2[623LL/AA] and HA-ClC-2[635LL/AA] mutants. (D) Cartoon representation of p75-ClC-2ct chimera constructed by fusing the luminal, transmembrane, and eight cytoplasmic residues of p75 with the entire C-terminus domain (347 amino acids) of ClC-2. The single N-linked glycan and four O-linked glycans of p75 are displayed. (E) Stable MDCK cells lines expressing WT p75-ClC-2ct or the dileucine mutants p75-ClC-2ct[623LL/AA], p75-ClC-2ct[635LL/AA], and p75-ClC-2ct[812LL/AA]. Cells were cultured for 4 d on Transwell filters, fixed without permeabilization, and immunolabeled with mouse antibodies to the ectodomain of p75 (green) to visualize the surface distribution of the chimeric proteins. Note the basolateral localization of WT p75-ClC-2ct and p75-ClC-2ct[812LL/AA] and the apical redistribution of p75-ClC-2ct[623LL/AA] and p75-ClC-2ct[635LL/AA].