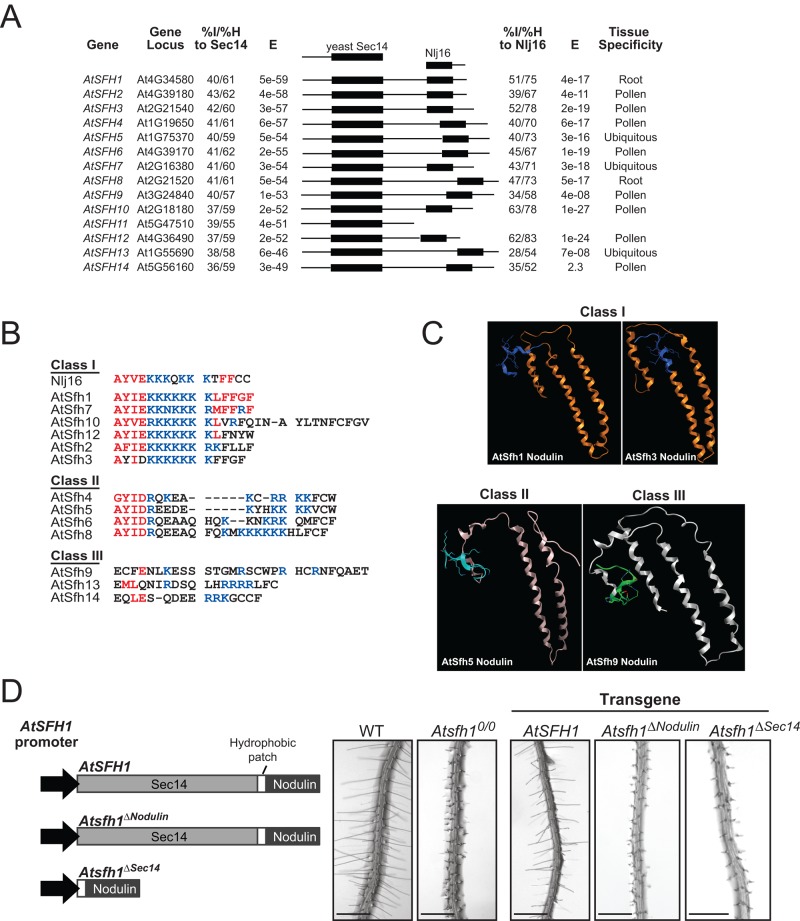
FIGURE 1:
The Arabidopsis Sec14-nodulin protein family. (A) Alignment of the 14 highest-scoring Sec14 homologues of the Arabidopsis Sec14-like PITP family. All Arabidopsis proteins with homology to the L. japonicus Nlj16 nodulin are also shown. Percentage identities (% I) and similarities (% H) and corresponding E-values are indicated (Sec14, left; nodulin, right), as are tissue expression profiles (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). (B) Alignments of the C-termini of class I, II, and III nodulin domains. Conserved residues and basic amino acids are in red and blue, respectively. (C) Homology models for nodulin domains. Models were generated by structural templating using nodulin homology to a region of a DNA topoisomerase. (D) Diagram of Atsfh1 constructs used to transform Atsfh10/0 plants. All transgenes were expressed under native AtSFH1 promoter control and encoded epitope-tagged myc-AtSfh1–hemagglutinin (HA), myc-AtSfh1ΔNodulin-HA, and AtSfh1ΔSec14-HA, respectively. Bright-field images of root hairs of transgenic seedling. Scale bars, 1 mm.