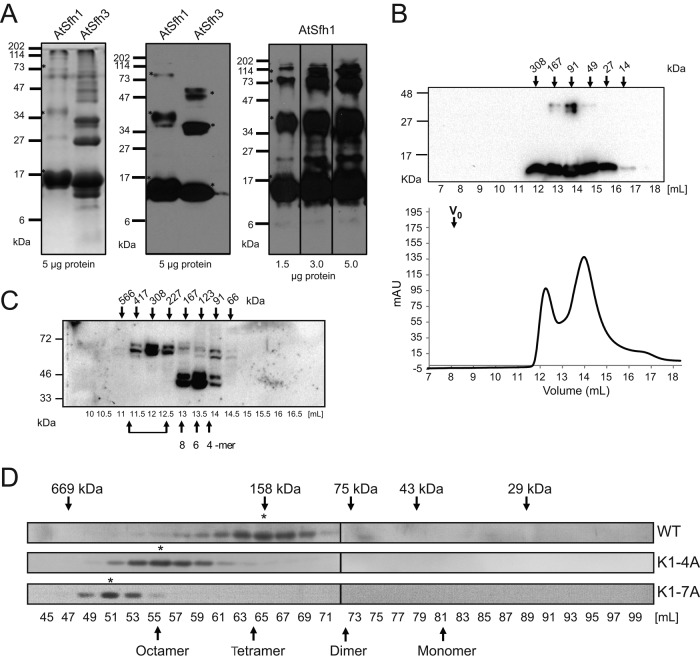
FIGURE 7:
Homo-oligomerization of class I nodulins. (A) Purified recombinant histidine (His)-tagged AtSfh1 (solubilized in 8 M urea) and soluble AtSfh3 nodulins (5 μg) were resolved by SDS–PAGE and visualized by Coomassie blue staining (left) and immunoblotting with anti-His tag antibody (middle). Right, immunoblotting of purified AtSfh1 nodulin with polyclonal AtSfh1 nodulin antibody (load at bottom). SDS-resistant homo-oligomeric forms are identified in all panels (asterisks). (B) Gel filtration chromatogram for purified native AtSfh3 nodulin. Top, immunoblot profile across the elution, shown above the chromatogram; elution properties of the indicated standards are identified by arrows. (C) Immunoblots of gel filtration column fractions of total lysates from yeast expressing myc-tagged AtSfh1 nodulin. Bottom, elution volume (milliliters); top, corresponding apparent molecular masses. Presumptive oligomeric states are identified at bottom. Brackets denote higher-order complexes. (D) Immunoblot profiles of gel filtration column fractions of lysates from tobacco leaf tissues expressing mRFP-tagged AtSfh1 WT, AtSfh1K1-4A, and AtSfh1K1-7A nodulins using anti-mRFP antibodies to visualize nodulin chimeras. Peak fractions of homo-oligomeric forms are identified (asterisks). Monomeric and presumed homo-oligomeric forms of the mRFP-tagged proteins are identified (arrows).