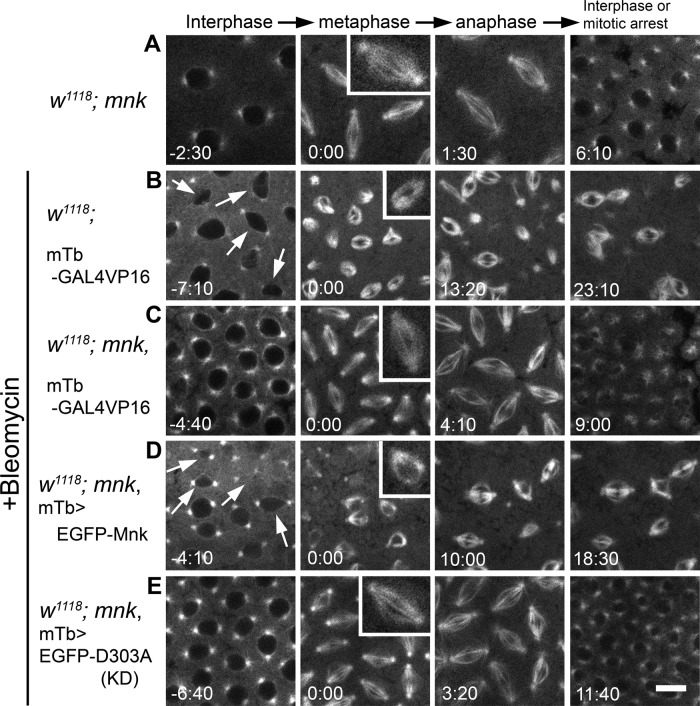
FIGURE 2:
EGFP-Mnk restores DNA damage responses in mnk mutant embryos during the syncytial blastoderm stage. All frames are from the rhodamine channel. (A) An mnk mutant embryo injected with rhodamine-tubulin. Normal spindles formed (inset), and a timely exit from mitosis occurred. Selected frames from Supplemental Movie S2. (B) An embryo wild type for mnk carrying a P[mTb-GAL4VP16] transgene was injected with bleomycin and rhodamine-tubulin. Anastral spindles formed (inset), and mitotic delay (or arrest) occurred. Arrows indicate dropping nuclei from the cortex. Selected frames from Supplemental Movie S3. (C) An mnk mutant embryo carrying a P[mTb-GAL4VP16] transgene was injected with bleomycin and rhodamine-tubulin. Normal spindles formed (inset), and a timely exit from mitosis occurred. Selected frames from Supplemental Movie S4. (D) An mnk mutant embryo expressing EGFP-Mnk was injected with bleomycin and rhodamine-tubulin. Anastral spindles formed (inset), and mitotic delay/arrest occurred. Selected frames from Supplemental Movie S5. Arrows indicate dropping nuclei from the cortex. (E) An mnk-null embryo expressing EGFP-D303A was injected with bleomycin and rhodamine-tubulin. Normal spindles formed (inset), and a timely exit from mitosis occurred. Selected frames from Supplemental Movie S6. Elapsed time is shown in minutes:seconds. Scale bar, 10 μm.