Fig. 3.
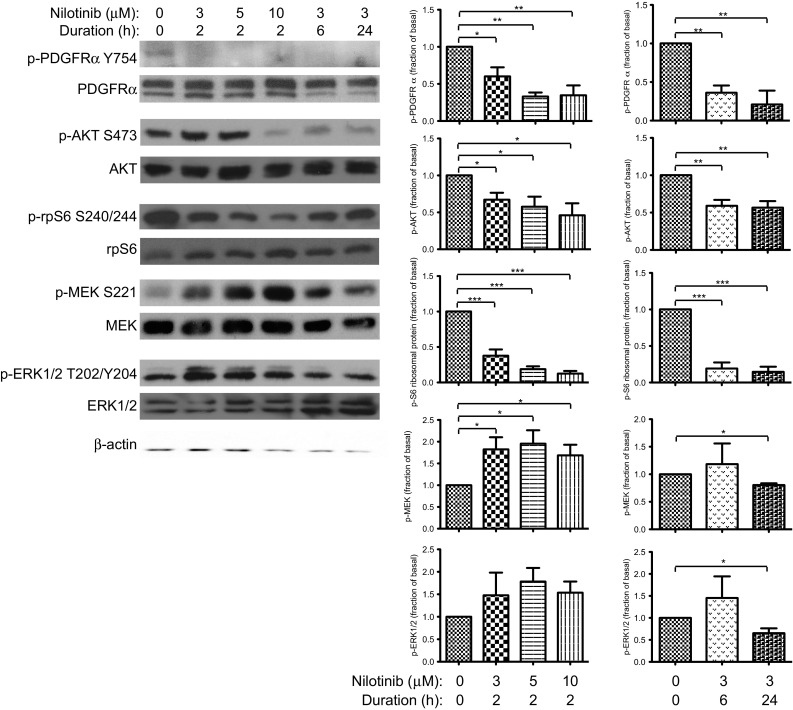
Nilotinib inhibits PDGFRα and the AKT and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. SJ-G2 cultures in 10 % FBS-supplemented growth media were exposed to nilotinib 0–10 μM for 2 h, and to 3 μM for up to 24 h. Phosphorylation of PDGFRα, AKT, S6 ribosomal protein, MEK and ERK1/2 was analyzed by Western blotting. β-actin is loading control. Accompanying bar graphs display relative phosphorylation in each condition, compared with basal levels (0 μM nilotinib vehicle treatment). Significant difference is indicated by * for p < 0.05, ** for p < 0.01, and *** for p < 0.001. Basal phosphorylation of all proteins was demonstrated. Exposure to nilotinib resulted in reduction of PDGFRα phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of AKT and S6 ribosomal protein was also decreased, and continually suppressed with extended inhibitor treatment. Phosphorylation of MEK was initially increased, but sustained exposure to nilotinib resulted in suppression below baseline. ERK1/2 activation was decreased following 24 h of nilotinib treatment
