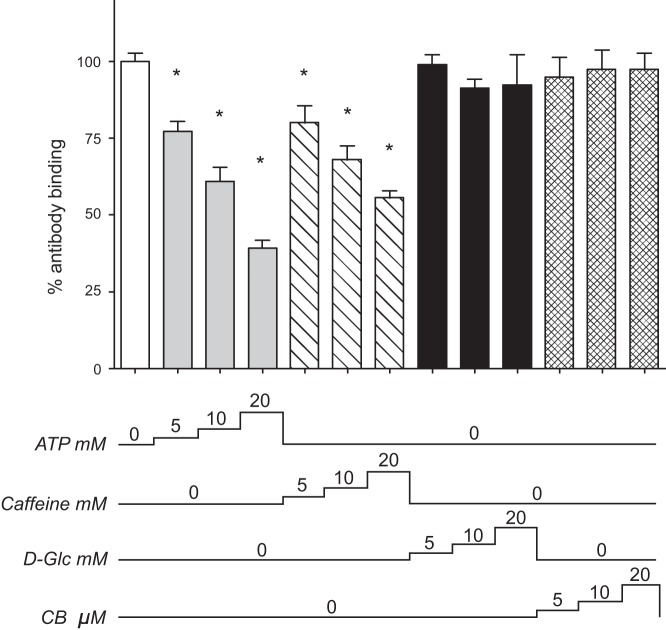
Fig. 4.
Caffeine and ATP promote conformational change in the GLUT1 COOH terminus. Ordinate: COOH-terminal antibody (C-Ab) binding to GLUT1 measured by ELISA (relative antibody binding, %); abscissa: C-Ab binding conditions. C-Ab binding to unsealed GLUT1 proteoliposomes was measured in the presence and absence of ATP (5–20 mM, gray bars), caffeine (5–20 mM, diagonal bars), d-glucose (d-Glc, 5–20 mM, black bars), or CB (5–20 μM, hatched bars). The numbers below the chart indicate the concentration of ligand present during the binding assay. Results are shown as means ± SE of 3–16 measurements made in duplicate. *Unpaired, 1-tailed t-test analysis indicates that the results are significantly less than that observed in control antibody binding (P ≤ 0.0027).