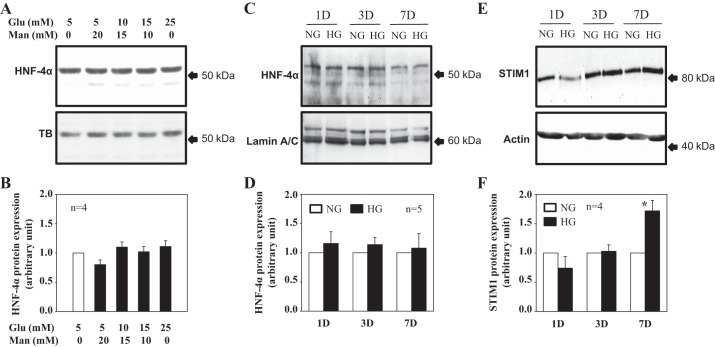
Fig. 4.
High glucose (HG) effect on HNF4 and STIM1 protein expression in cultured human MCs. A–D: Western blot analysis showing HNF4α protein expression in response to different concentrations of glucose (Glu; A and B) and different time periods of HG treatment (C and D). In A and B, whole cell lysates were used. MCs were cultured in 0.5% FBS medium containing different concentration of glucose for 3–4 days. Appropriate concentrations of α-mannitol (Man) were used as an osmotic control. In C and D, nuclear extracts were used. MCs were incubated in 0.5% FBS containing normal glucose (NG; 5.6 mM glucose + 20 mM mannitol) and HG (25 mM glucose) for 1 day (1D), 3 days (3D), and 7 days (7D). A and C: representative immunoblots. TB and lamin A/C were used as loading controls. B and D: summary data from experiments shown in A and C, respectively. HNF4α protein expression levels were normalized to TB (B) or lamin A/C (D) and then further normalized to either group of 5 mM glucose with 0 mM mannitol (B) or the NG group of each HG treatment time period (D). n is the number of independent experiments. E and F: time course effect of HG treatment on STIM1 protein expression (whole cell lysates). MCs were incubated in 0.5% FBS containing NG (5.6 mM glucose + 20 mM mannitol) and HG (25 mM glucose) for 1, 3, and 7 days. Actin served as a loading control. STIM1 protein expression levels were normalized to actin and then further normalized to the NG group of each HG treatment time period. *P < 0.05 compared with the NG group with 7-day treatment. n is the number of independent experiments.