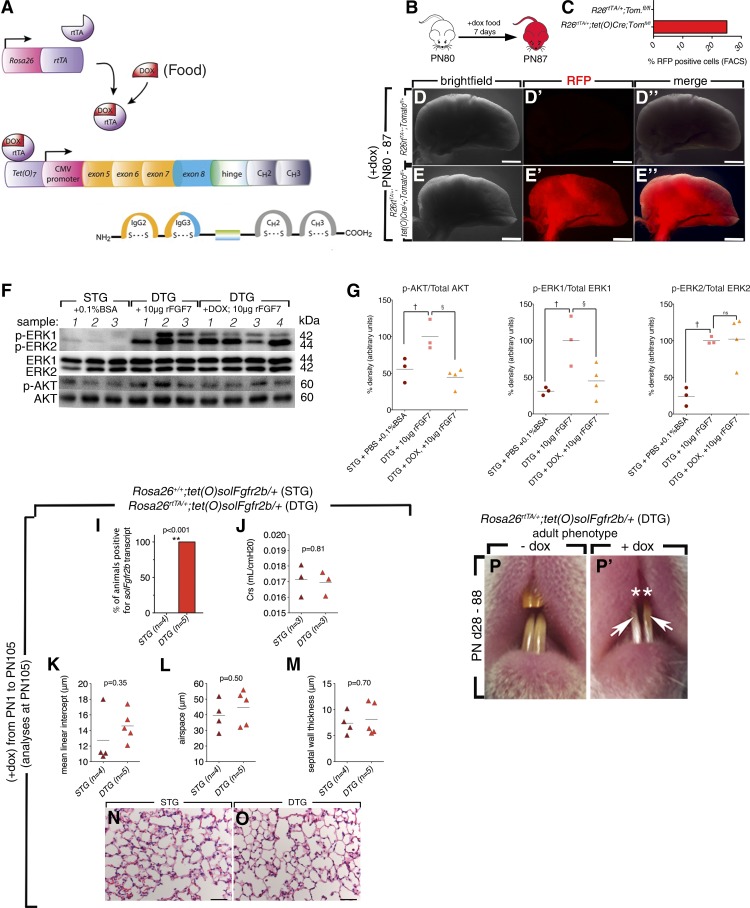
Fig. 2.
Validation of Rosa26rtTA/+;tet(O)sFgfr2b/+ [double-transgenic (DTG)] mice. The Rosa26 promoter drives ubiquitous expression of reverse tetracycline transactivator (rtTA), which in the presence of doxycycline (dox) binds a tetracycline response sequence. Binding results in the activation of a CMV promoter, which drives expression of a chimeric transgene containing the extracellular binding domain of Fgfr2b fused with the heavy chain domain of IgG (A). Lung-specific efficiency of Rosa26 promoter was tested in Rosa26rtTA/+;tet(O)Cre/+;Tomatofl/+ mice fed +dox-food for 7 days (B and C). Red fluorescent protein (RFP) expression was detected in ∼25% of total cells by FACS and in none of the cells in mice lacking the tet(O)Cre transgene as illustrated by fluorescence stereomicroscopy (D–E″). Single-transgenic (STG) mice (n = 3) received 50 μl of PBS with 0.1% BSA; DTG mice were fed normal food (n = 3) or +dox food (n = 4) for 1 wk and were given an intratracheal dose of 10 μg of FGF7. At 30 min later, the lysates were collected and blotted for p-Akt and p-Erk1/2 signals (F). +dox DTG mice blocked FGF7-mediated p-Akt (G) and p-Erk1 signals (H), p-ERK2 (H′) remained elevated (F–H′). †Significant; §very significant. The chimeric transcript was detected only in DTG mice (I) and lung compliance was not changed in DTG mice fed +dox food from postnatal day (PN) 1 to PN105 (J). **Very significant. K–O: morphometric analyses were performed on these mice, and in concurrence with previous studies no significant differences in mean linear intercept, air space, or septal wall thickness were observed in DTG mice. Adult DTG mice fed +dox food from PN28-88 failed to regenerate maxillary incisors (P–P′).