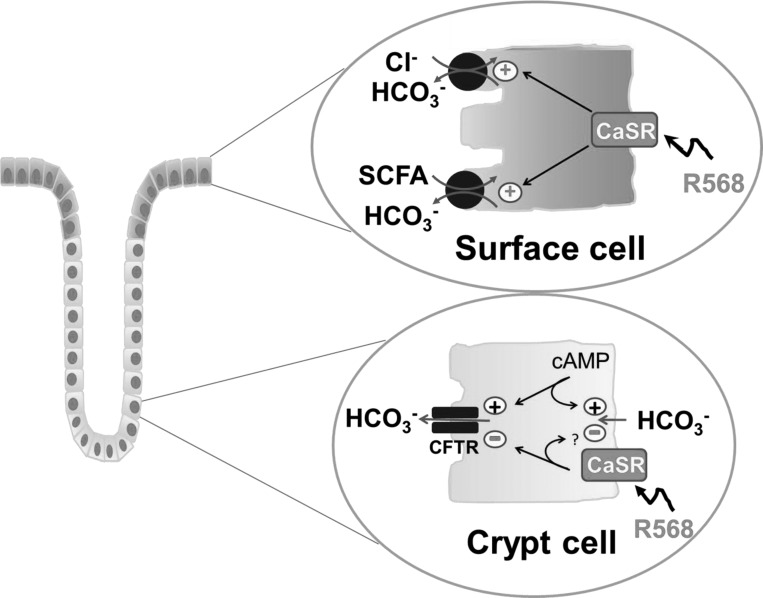
Fig. 8.
Cellular model of CaSR regulation of HCO3− secretion in colonocytes of rat distal colon. Top: R568 acting via CaSR causes enhancement of HCO3− secretion in surface epithelial cells by stimulation of luminal Cl−-dependent HCO3− secretion via apical Cl−/HCO3− exchange and stimulation of luminal SCFA-dependent HCO3− secretion mediated by apical SCFA/HCO3− exchange. Bottom: CaSR reduces HCO3− secretion in the crypt epithelial cells through inhibition of a cAMP-dependent HCO3− secretory process that may involve a 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)benzoic acid/glibenclamide-sensitive apical anion channel such as cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and/or a basolateral HCO3− entry mechanism(s). +, stimulation; -, inhibition.