Figure 2.
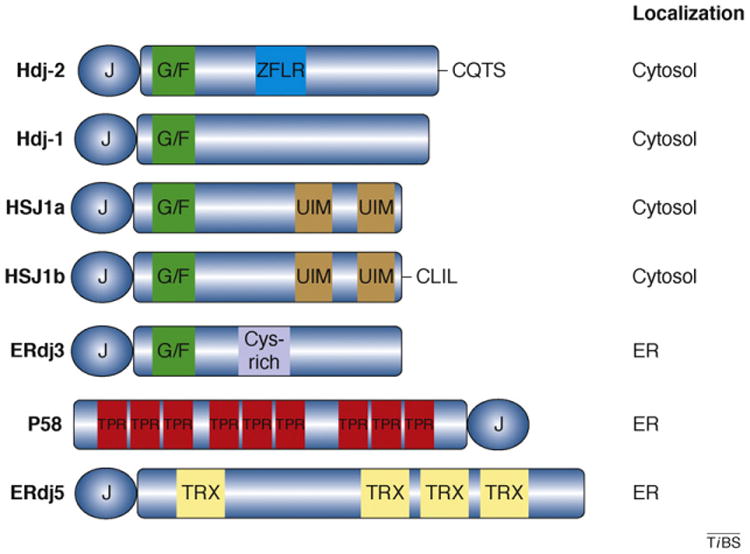
Domain structures of several human Hsp40s. Type I Hsp40s such as Hdj-2 (also called DnaJA1) possess a J-domain, G/F-rich region (green) and a ZFLR (blue). Hdj-2 is distinct from many Hsp40s because it is farnesylated at a C-terminal CAAX motif (CQTS). Type II Hsp40s, such as Hdj-1 (also called DnaJB1), lack the ZFLR. HSJ1a and HSJ1b (also called DnaJB2) are neuron-specific type II Hsp40 isoforms. Both isoforms possess two ubiquitin interaction motifs (UIMs; brown); however, Hsj1b also contains a CAAX motif that is geranylgeranylated (CLIL). ER-localized Hsp40s have also evolved specialized domains. For example, ERdj3 (also called DnaJB11) contains a cysteine-rich motif (purple) in the C terminus [21]. P58 (also called DnaJC3) contains nine tetratricopeptide repeats (TPR; red) that might bind non-native polypeptides, whereas ERdj5 contains three thioredoxin (TRX; yellow) domains, which are responsible for disulfide reductase activity. The length of each Hsp40 represents its relative size. The intracellular location of each Hsp40 is noted.
