Figure 2. Effect of topographic region of pressure recording and distinct manometry catheters on pressure drift (PD).
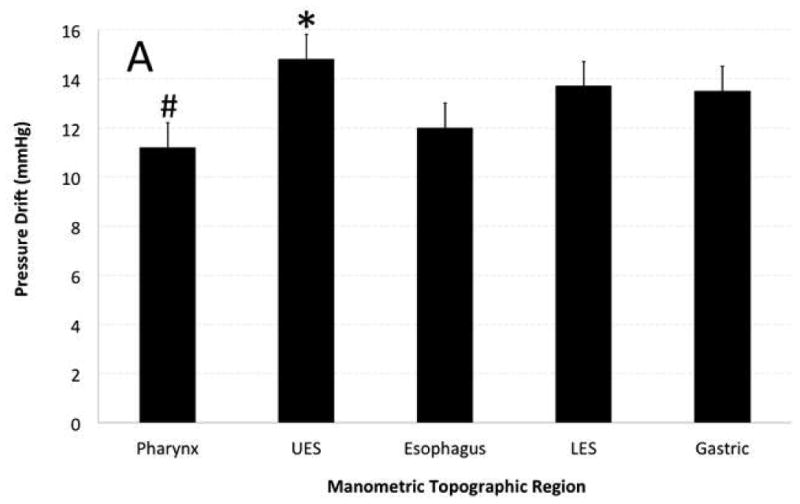
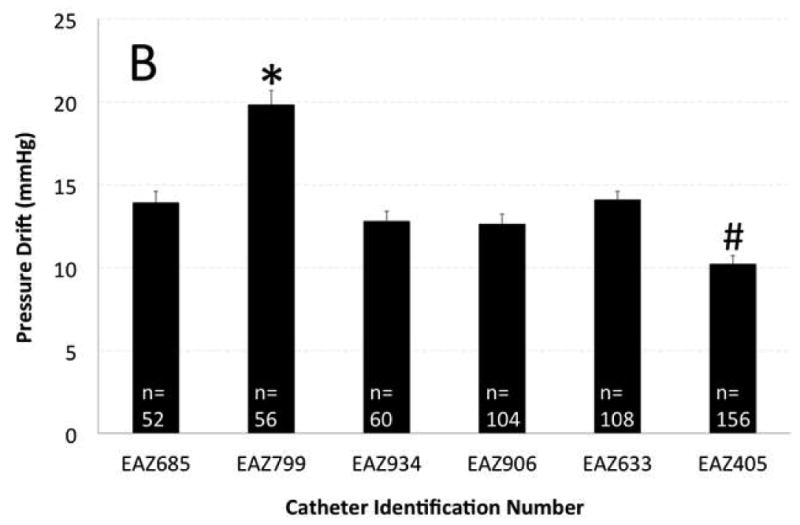
A) Topographic region of pressure recording showed significant effect on PD. UES showed highest and pharynx showed lowest amount of PD that was statistically different from other topographic regions. B) Catheter EAZ799 showed highest and catheter EAZ405 showed lowest PD than remainder of manometry catheters. Catheter EAZ 405 had the most clinical manometry use and EAZ799 was one of the less utilized manometry catheters.
