Figure 4. High mobility group (HMG) boxes in nucleosome remodeling.
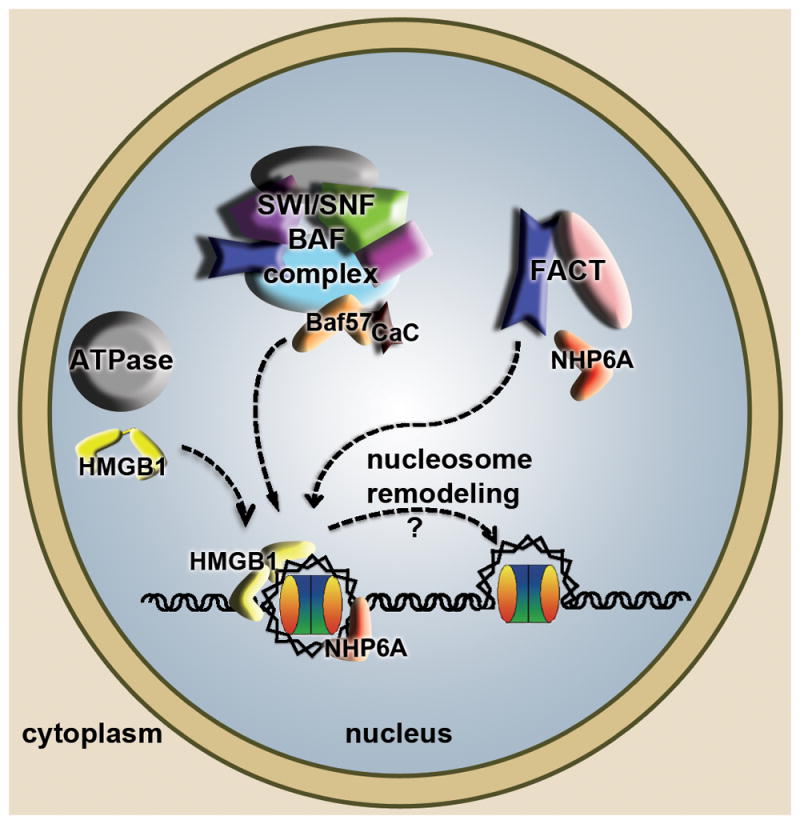
The diagram summarizes and combines findings from S. cerevisiae and other eukaryotes. HMGB proteins in metazoans (yellow) and NHP6A in S. cerevisiae (red), in their individual cellular contexts can bind to nucleosomal DNA and assist ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers (grey) in loosening DNA and providing access to other DNA dependent machineries. Related SWI/SNF (in S. cerevisiae) and BAF (in metazoans) complexes harbor an HMG box containing subunit BAF57 (orange) that promotes nucleosome remodeling, in some cases requiring binding of calcium calmodulin (CaC in black). The histone chaperone FACT has three subunits in S. cerevisiae (Spt16, Pob3, NHP6A), of which NHP6A promotes the association of the FACT complex with nucleosomes to facilitate remodeling.
