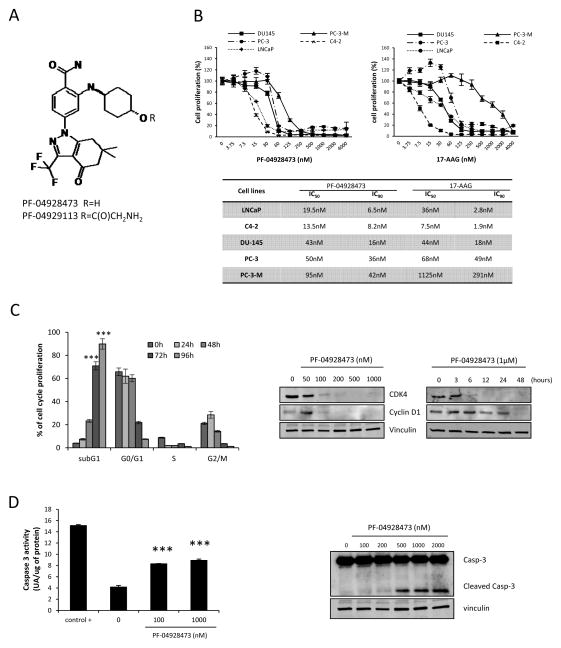
Figure 1. PF-04928473 inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines.
A, chemical structure of PF-04928473 (active molecule) and PF-04929113 (pro-drug). B, tumor cell lines (LNCaP, C4-2, DU145, PC-3 and PC-3-M) were cultured for 72 hours in the presence of PF-04928473 or 17-AAG at the indicated concentration and cell growth was determined by crystal violet assay and compared with control. The table compares the IC50 and IC90 of each tumor cell lines between PF-04928473 and 17-AAG. C, left, LNCaP cells were treated with 1μM of PF-04928473 for 2 days, and the proportion of cells in subG1, G0-G1, S, G2-M was determined by propidium iodide staining. C, right, LNCaP cells were treated with PF-04928473 at indicated concentration for 2 days, and CDK4 and cyclin D1 expression levels were measured by Western blotting. D, left, LNCaP cells were cultured in presence of 1μM PF-04928473 for 2 days. Caspase-3 activity was determined on the cell lysates and the results are expressed in arbitrary units and corrected for protein content. ***, p<0.001. D, right, LNCaP cells were treated with 1μM PF-04928473 for 2 days and Caspase 3 expression level was assessed by Western blotting. All experiments were repeated at least thrice.