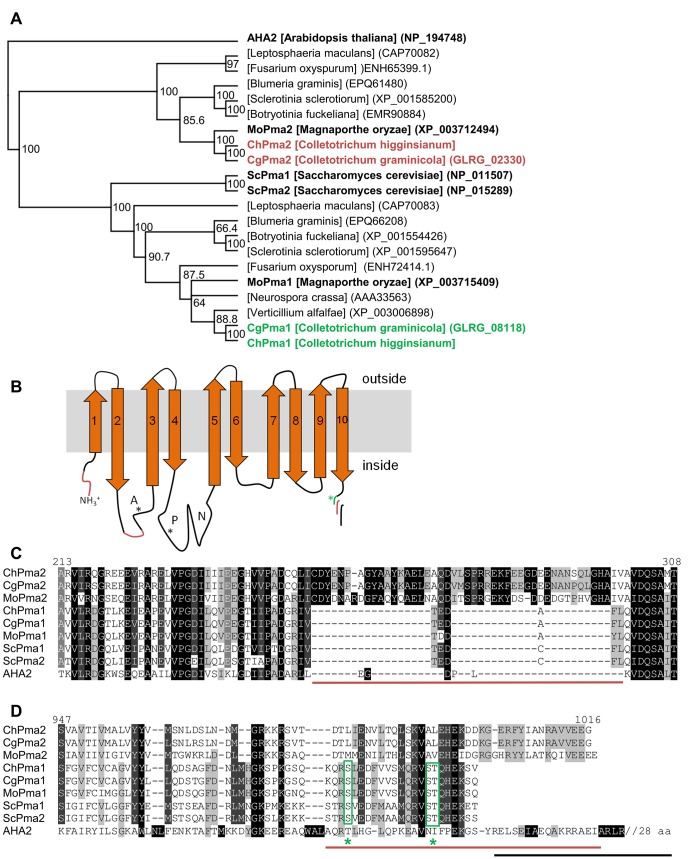
Fig 8. Fungal H+-transporting P-type ATPases.
(A) Phylogenetic analysis of plasma membrane H+-ATPases. Sequences were aligned with ClustalW and the tree was generated by Geneious treebuilding (Jukes-Cantor; Neighbor-joining) with AHA2 from A. thaliana as outgroup. Bootstrap values (1000 replicates) are indicated as percentage at the right side of the nodes. (B) Schematic illustration of the domain structure of H+-P-type ATPases as found in AHA2 (A: actuator domain, P: phosphorylation domain, N: nucleotide binding domain). Regions specific for ChPma2-like proteins are depicted in red. The green asterisk marks regulatory phosphorylation sites in yeast Pma1. The variable C-terminus is illustrated in red for ChPma2-like proteins, in green for Pma1-like proteins and in black for the autoinhibitory region of Arabidopsis AHA2. (C/D) Amino acid sequence alignment of Pma1 and Pma2 proteins from Colletotrichum higginsianum (Ch), Colletotrichum graminicola (Cg), Magnaporthe oryzae (Mo), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc) and Arabidopsis thaliana (AHA2). (C) Cytoplasmic region between transmembrane domains two and three. (D) C-terminal region. Potential regulatory serine and threonine residues are marked with green asterisks.