Figure 5.
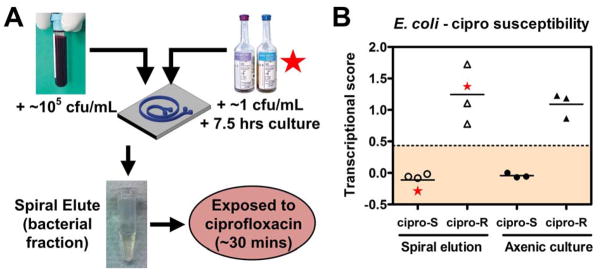
Antibiotic susceptibility determination of pathogens from blood after DFF by mRNA recognition. (A) Schematic of experimental approach: whole blood spiked with E. coli at 105 cfu/mL, or BACTEC blood cultures grown from 1 cfu/mL to >105 cfu/mL of E. coli, were processed by DFF, and the recovered bacteria were concentrated, then exposed to ciprofloxacin at 2.5 mcg/mL for 30 minutes at 37 °C, lysed, and detected by the NanoString assay using a probeset directed against ciprofloxacin-responsive mRNAs (see Methods for details). (B) Transcriptional susceptibility scores (see Methods for details) from E. coli inoculated into whole blood (left panel, open symbols) compared with axenic culture controls (right panel, closed symbols), each from ciprofloxacin-resistant (circles) vs ciprofloxacin-responsive (triangles) E. coli strains. Star symbols depict data from one susceptible (at left) and one resistant (at right) E. coli strain grown in BACTEC blood culture bottle. Dashed horizontal line represents four standard deviations from the mean transcriptional susceptibility score of the derivation cohort of susceptible E. coli strains.
