Figure 2. A model for the dual roles of IL-10 in PV during active disease and remission after B cell depletion therapy.
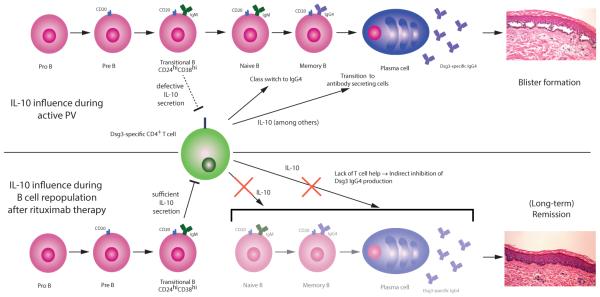
In active disease, IL-10 favors class switch to IgG4, the characteristic PV autoantibody subclass. Additionally, B cell differentiation into antibody secreting cells is promoted by IL-10, which results in higher anti-Dsg3 antibody concentrations, leading to disease symptoms. Bregs in active PV are defective, with reduced IL-10 secretion and inability to suppress CD4+ T cell responses, which perpetuates the autoimmune reaction. After B cell depletion with rituximab, repopulating CD24hiCD38hi transitional B cells produce IL-10 that can inhibit CD4+ T cells, thereby preventing the stimulation of pathogenic anti-Dsg3 B cell populations, leading to disease remission.
