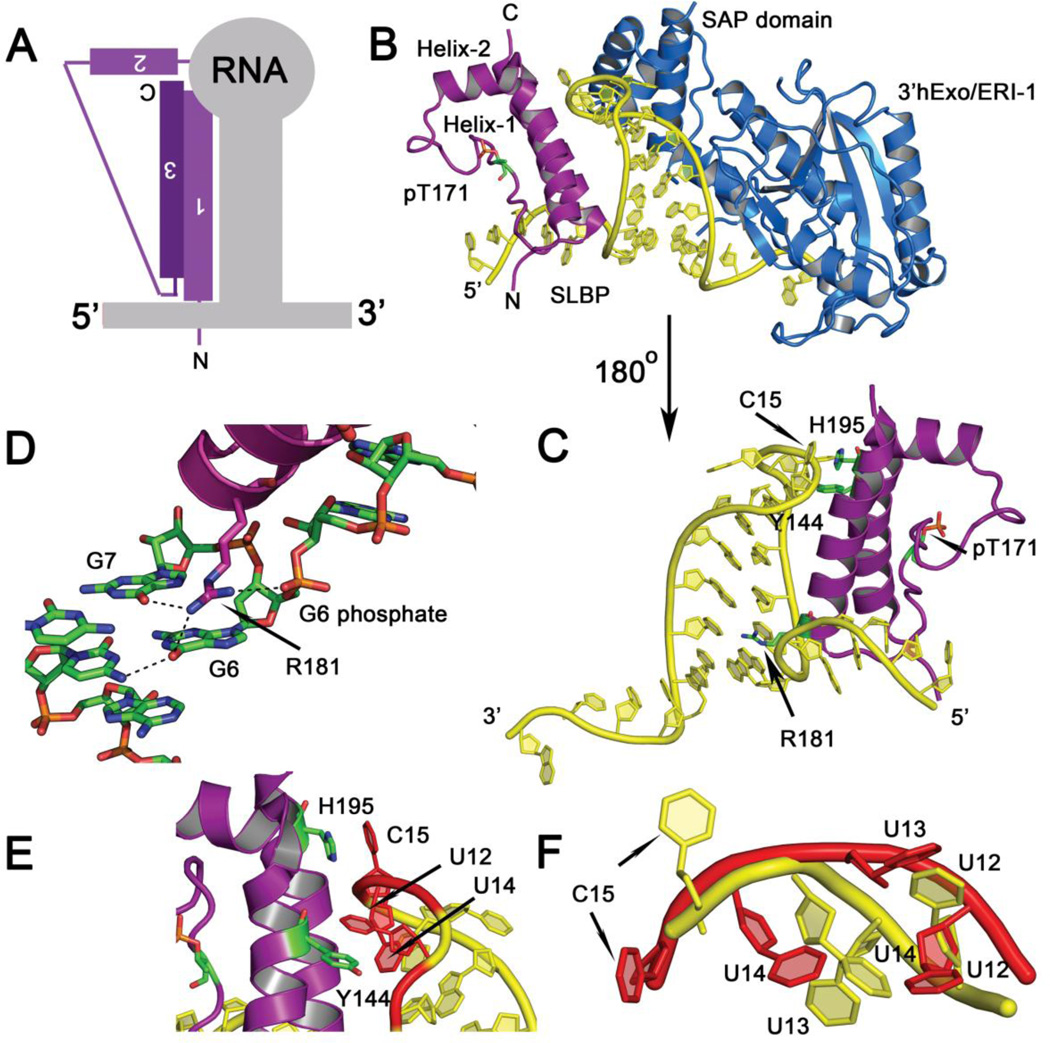
Figure 3.
(A) Summary schematic showing the mode of histone mRNA stem-loop recognition by the SLBP L-motif. (B) Crystal structure of the Thr171 phosphorylated SLBP-histone mRNA stem-loop-3’hExo/ERI-1 ternary complex (PDB code 4QOZ). SLBP is in purple, the RNA in yellow, and the exonuclease 3’hExo in blue. The SAP domain of 3’hExo contacts the tetraloop on the opposing face from SLBP. The orientation shown is from the 5’ end of the RNA to the 3’ end. (C) The back view (180° rotation from (B)) of the SLBP RNA complex is shown. For clarity, 3’hExo is not displayed. The three side chains (R181, Y144, and H195) that contact RNA bases or make stacking interactions are shown in green. (D) Hydrogen bonds mediated by the guanidinium group of R181 to the O6 of G6 and G7 at the base of the stem and the phosphate of G6 is shown. (E) Base stacking interactions with U12 and U14 of the RNA tetraloop are depicted. (F) Superposition of the tetraloop structure of free RNA tetraloop (PDB code 1JWC) (in red) and the tetraloop in the RNA complex (4QOZ) (in yellow). The uridines are flipped out and the tetraloop structure unfolded in the protein bound state.