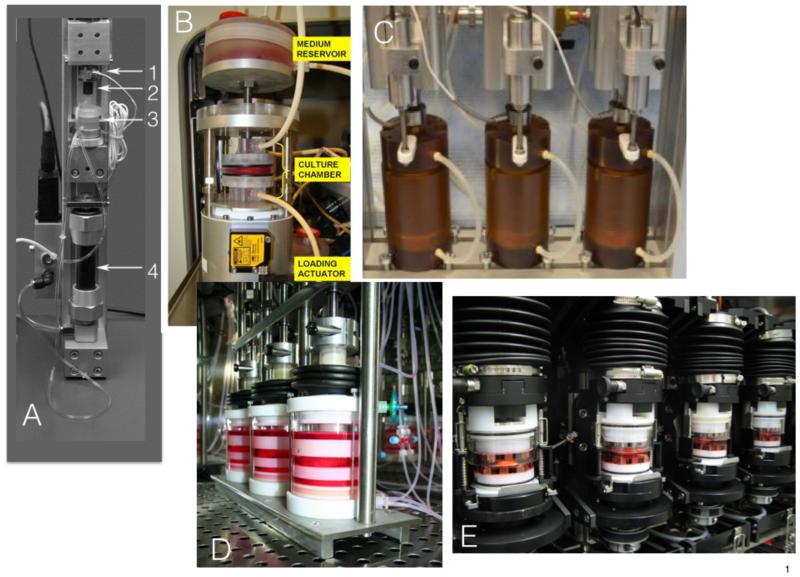
Figure 3. Five examples of Bioreactors recently published by different research teams.
A. Polycarbonate chamber with gas-permeable silicon membrane [36,37]. Key feature: media refreshment system with tubing; culture of IVD with BEP, a steel ball in the axis to ensure parallel and even force transition. 1. Force cell, 2. Coupling with steel ball, 3. Polycarbonate culture chamber, 4. Pneumatic actuator “fluidic muscle”. B. Polycarbonate culture system to allow IVD culture with BEP; key feature: perfusion of culture media through large medium containers [31]. C. Key feature: high force hydraulically actuated bioreactor, Instrumented with load cells and inductive way sensors to allow measurements of IVD height and mechanics throughout testing and culture, chambers are made from Ultem® [29]. D. Glass and Polyoxymethylen (POM) press fit design with uniaxial compression. key feature: specialized adjustments to allow bovine and human IVD culture [33]. E. Glass and POM bioreactor [32]; key feature: presence of serrated titanium plates to allow torsion and compression, special release mechanism to hook and un-hook the bioreactor stations.