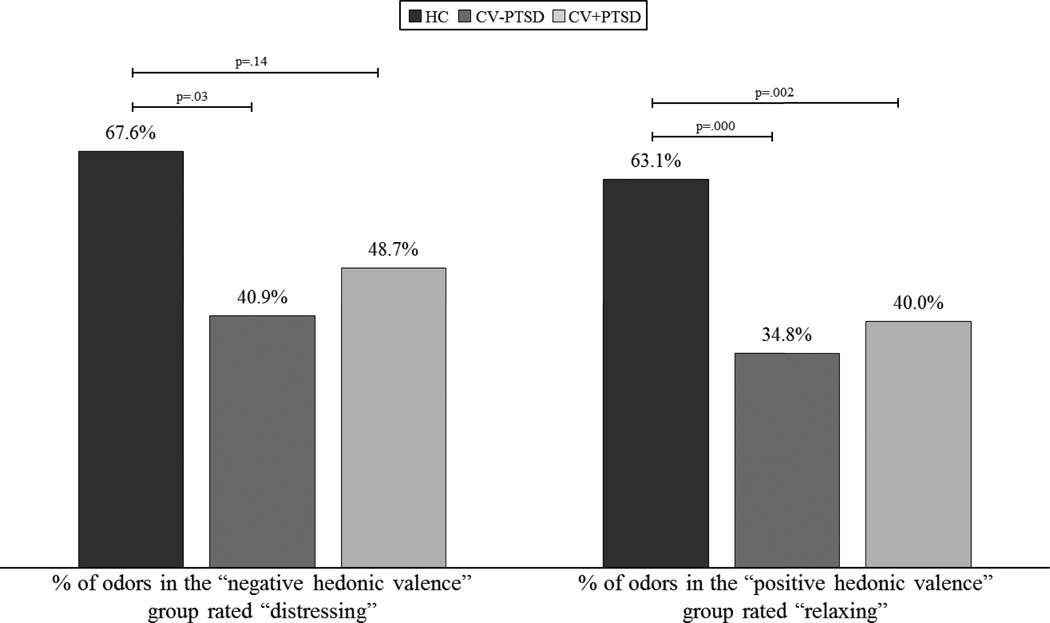
Figure 3. Group differences in the percentage of odors rated to be “distressing” or “relaxing” within the negative and positive hedonic valence groups.
demonstrates that combat veterans with and without PTSD (CV+PTSD, CV-PTSD, respectively) compared to healthy controls (HC) report overall reduced sensitivity not only to the distressing properties of odors with negative hedonic valence (that are non-trauma-related), but to the relaxing properties of odors with positive hedonic valence.